Background
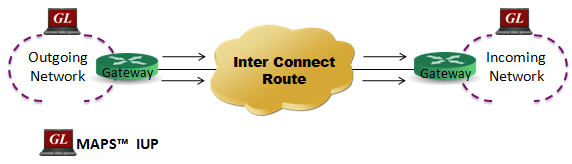
The SS7 (C7) IUP is UK national standard protocol used to interconnect two Public Network Operators. The IUP feature was derived from the standards of the Public Network Operators - Interconnect Signaling Committee (PNO-ISC).
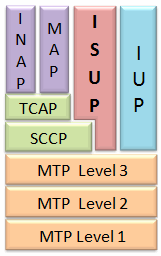
The IUP comprises a number of call set up, release, and supervision protocols which provide additional Call Control Procedures. The call setup protocols are used to perform bearer establishment and call establishment procedures. The call release protocol is used to perform bearer release procedure. The supervision protocols are used to exchange call status information between networks.
Overview
GL’s Message Automation & Protocol Simulation (MAPS™) is a powerful Protocol Test platform-supporting a wide range protocols such as SS7 over TDM (T1/E1), ISDN over TDM, GSM A interface & GSM A bis interface over TDM, Megaco, SIP, MGCP, SIGTRAN and others over IP.
MAPS™ IUP is an advanced protocol simulator used to simulate UK specific SS7 IUP in British Telecom (BT) networks. It is designed to simulate interconnect route between Incoming and Outgoing Networks as defined by the PNO-ISC/INFO/004(IUP) and TGS/SPEC/006 specifications. MAPS™ IUP functionality covers the UK variant of SS7 implementing MTP2, MTP3 protocol standards over TDM (T1/E1) transport layer. Ready scripts are available supporting various protocol services including Basic Call Service protocol (IFAM, IAM, ACI, Bearer Establishment), Request Service protocol, Nodal End-to-End Data protocol, Enveloped ISUP Essential Service protocol, and ISDN Call Handling Service protocol.
The tester supports testing network elements, error tracking, regression testing, conformance testing, load testing/call generation and generation of high volumes of traffic. It is able to run pre-defined test scenarios against ISUP test objects in a controlled & deterministic manner.
The MAPS™ IUP supports powerful tools like Message Editor, Script Editor and Profile Editor which allow new scenarios to be created or existing scenarios to be modified using ISUP messages and parameters. It gives the flexibility of modifying any message so that we can easily duplicate the messages generated by any node to resolve interoperability issues.
GL also provides an independent GUI based SS7 protocol analyzer for online capture and decode of the signaling in real-time both during tests and as a stand-alone tracer for live systems.
Possible applications include:
- Multi-protocol, Multi-interface Simulation
- Provides fault insertion, and erroneous call flows testing capability
- Performance testing, Load testing, Functional testing, Regression testing and Conformance testing of network elements
- Ready scripts makes testing procedure simpler, less time consuming and hence time to market products
- Test response of network against protocol message modification, or corruption
- Inter-operability testing of networks
Main Features
- IUP simulation over TDM (T1/E1)
- Multiple T1/E1 line interfaces supported
- Supported procedures include Basic Call Service protocol (IFAM, IAM, ACI, Bearer Establishment), Request Service protocol, Nodal End-to-End Data protocol, Enveloped ISUP Essential Service protocol, and ISDN Call Handling Service protocol
- Supports generation & detection of TDM traffic - Auto Traffic Voice, Digits, Tones, IVR, FAX, Dynamic VF, and User-defined traffic
- User-friendly GUI for configuring the SS7 MTP Layers
- User Configurable Signaling Links
- User-configured Circuit Mapping, i.e., defines Circuit Identification Codes (CIC) and map these CICs to Timeslots/Trunks in order to enable Voice/Data traffic
- Supports MTP2 and MTP3 protocol machine
- Multiple MTP links
- Supports client-server functionality through Command Line Interface (CLI) such as the Python, and TCL (requires additional license)
- Supports scripted call generation and automated call reception
- Provides protocol trace with full message decoding, and graphical ladder diagrams of call flow with time stamp
- Provides call statistics with associated captured events and error events during call simulation
Supported Protocols Standards
Supported IUP Procedures
Listed below are the some of the IUP Procedures supported by MAPS™ IUP
- Basic Call Service: (Service Handling Protocol)
- IFAM Protocol
- IAM (SND) Protocol
- IAM (SAD) Protocol
- Subsequent Address Message (SAM)
- Final Address Message (FAM)
- IFAM Protocol
- Call Establishment
- IUP Basic Call Service: (Service Handling Protocol)
- Request Service protocol (Service Handling Protocol 2)
- SASUI Protocol (Supplementary Call Information)
- ACI Protocol (Supplementary Call Information)
- Nodal End-to-End Data Protocol (Service Handling Protocol 3)
- ISDN Call Protocol (Service Handling Protocol 1)
- Enveloped ISUP Essential (Service Handling Protocol 8)
- IUP Basic Call Service: (Service Handling Protocol)
- Call Supervision:
- Connection not completed – SUBSCRIBER ENGAGED or SUBSCRIBER OUT
- Connection not completed – SUBSCRIBER ENGAGED or SUBSCRIBER OUT
- Call Release Procedures
- Connection not completed – CNA procedures
- Connection not completed – RELEASE procedures
- Bearer Release Protocols
- Connection not completed – CNA procedures
Typical Call Flow
Shown below is the typical call procedure in IUP interfaces:
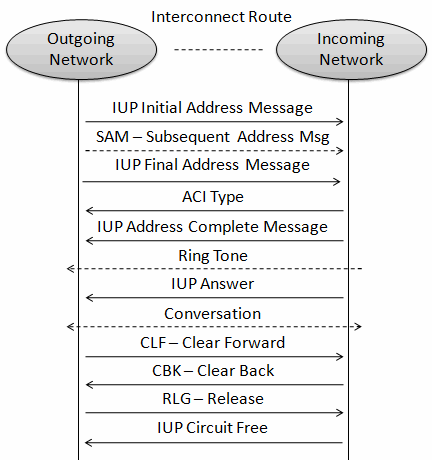
Basic (Telephony) Service Handling Procedure
Call Generation and Reception
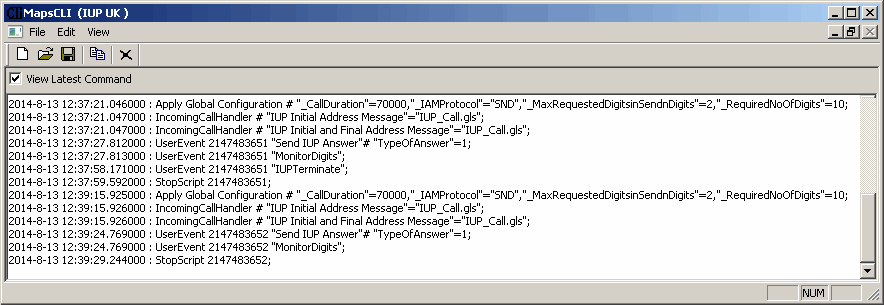
The screenshot below shows MAPS™ acting as Outgoing Network and initiating the procedure by sending the IUP Initial Address Message to Incoming Network, establishing an end to end connection between Incoming and Outgoing Networks suitable for telephony calls.
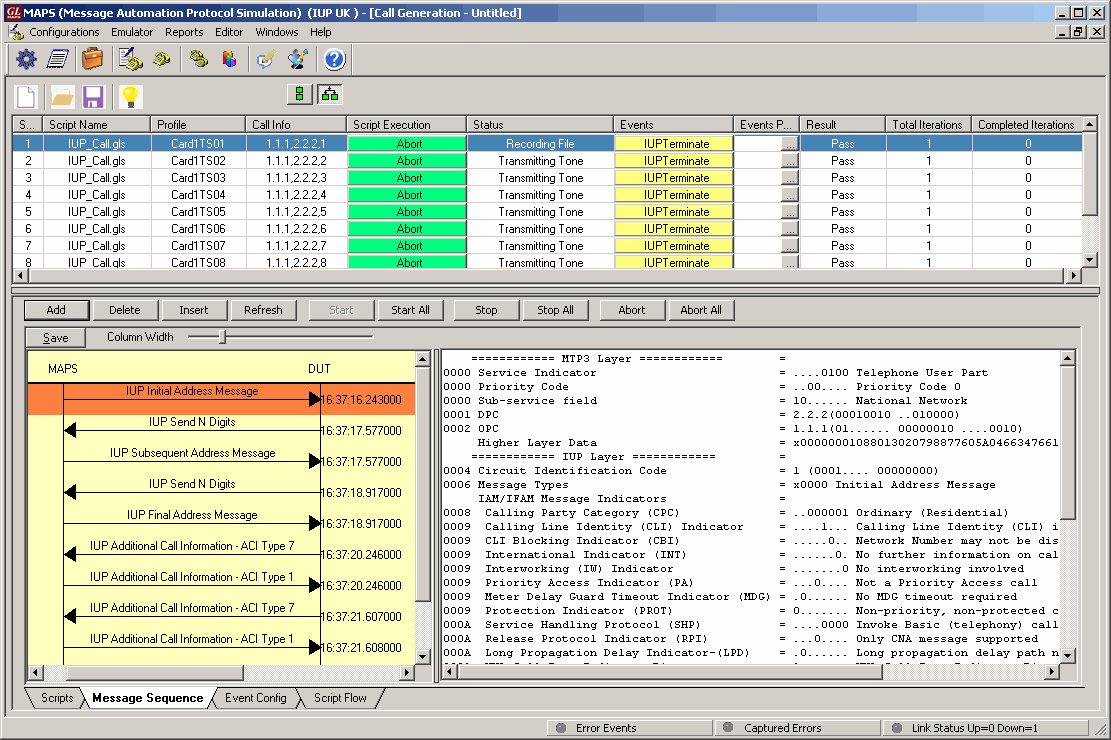
IUP Basic (Telephony) Call Generation
Call generated from other entity can be automatically detected in call reception window by pre-setting the required scripts in the Incoming Call Handler window.
The screenshot below shows MAPS™ IUP configured to act as Incoming Network terminal, which receives and responds to the incoming messages.
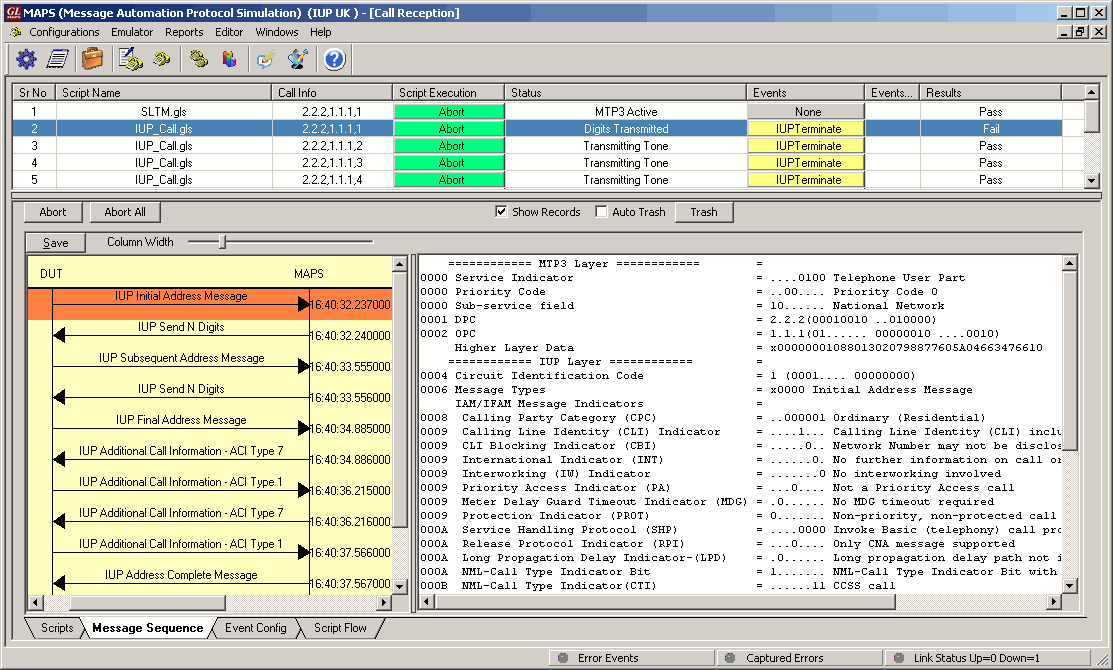
IUP Basic (Telephony) Call Reception
General MAPS™ Features
- Call Simulation & Control
- Multi-protocol, Multi-interface Simulation
- Script based and protocol independent software architecture
- Auto generate and respond to signaling messages
- Traffic Handling Capabilities (requires additional license)
- Fault Insertion, and Erroneous Call Flows Testing
- Automation
- Pre-processing tools
- Easy script builder for quick testing to advance testing
- Customization of test configuration profiles
- Unlimited ability to customize the protocol fields and call control scenarios
- Centralized Control and Remote Access
- Command Line Interface (requires additional license)
- Option to send reports to database accessible via web interface
- Centralized control of multiple MAPS™ applications remotely from single client application
- Reports and Statistics
- Call Status, Link Status, and Message Statistics
- Capture Events, and Error Events
Call Simulation and Control
The signaling and traffic simulation in a call is completely implemented using scripts. Commands in the scripts are executed in controlled way to simulate protocol and traffic behavior. Most of the commands used in the scripts are generic and independent of specific protocol.
MAPS™ application acts as either the Caller or resides at the network terminal acting as Callee. The Call Generation feature simulates an outgoing call by sending call control messages to the DUT using scripts and profiles. The profiles allow necessary parameters of call control messages to be changed during runtime. Call generated from other entity can be automatically detected in call reception window by pre-setting the required answer scripts in the Incoming Call Handler.
The call control scripts can also automatically handle the traffic over the established call. MAPS™ supports transmission and detection of various traffic types over IP (RTP, GTP), ATM, & TDM - such as, digits, voice file, single tone, dual tones, fax, sms, email, http, ftp, and video. MAPS™ also includes support for wide range of codec rates – visit www.gl.com/traffic-simulation.html and www.gl.com/voice-codecs.html webpage for more details.
Message Sequence - Each call scenario provides the trace with full decoding of the messages exchanged between the MAPS™ and the DUT, and graphical ladder diagrams of the call flow with time stamp. Impairments can be applied to messages to simulate error conditions that occur in real-time networks.
Event-Driven Control - Scripts execution, being event-based, allows redirection of script execution on-the-go with user-defined events. The custom parameters in the events can also be changed during script execution using event profiles.
Script Contents & Script Flow - The script flow and the contents window displays the Script Name, Sub-script Name, Script line number, and script statements to be successfully executed, which help the users in troubleshooting a particular call scenario.
Bulk Call Simulation and Load Testing
MAPS™ supports automated stress/load testing capabilities through Load Generation and Bulk Call Simulation features. Bulk Call Simulation allows quick configurations to easily create multiple test entries with different scripts and profiles. Multiple tests can be run simultaneously or sequentially (queue up tasks in succession). Load generation feature further allows specifying the patterns with which the bulk calls can be generated. Load generation can be customized with different statistical distribution patterns such as Uniform, Ramp, Sawtooth, Fixed, Normal, Step, and Step-Sawtooth distribution. Call duration also can be randomized using similar statistical distribution. This feature also helps users configure Stress/Load Testing parameters such as Call per second (CPS), Max Active Call, Minimum and Maximum Call Rates, Start Call Rates, and other parameters.
Scheduler
Scheduler can be used to schedule the simulation of bulk calls or manual calls at a specific start time. The pre-saved master configuration files for test setup and call simulation are automatically loaded to automate the test procedure.
Customization of Test Setup Parameters
The test setup profiles (.xml files) allow users to configure the necessary parameters in order to establish communication between MAPS™ and the DUT. It includes configuring parameters of the network nodes, the network properties, and transport related configurations such as T1/E1 timeslots, IP Address and port numbers for both MAPS™ and the DUT.
Once the transport layer is configured properly, protocol specific signaling messages and traffic can be transmitted and received successfully. All parameters setup in test setup are global and are accessible to all scripts. These parameters initialize protocol engines and the transport modules specific to the protocol.
Customization of Test Parameters, Call Flow, and Protocol Messages Using Pre-Processing Tools
- Message Editor - The Message Templates (GL’s proprietary *.HDL files) comprises of protocol encoding parameters with preset values. It is required to create a message template for every message in a protocol. The message templates are called within the scripts to perform scenario based testing.
- Profile Editor – Profiles (*.xml files) are used to change the values of the fields in the messages (i.e. Message Template in MAPS™) during the course of a call. The multiple profiles with varying parameter values that allow users to configure call instances in call generation and to receive calls.
- Script Editor - The script editor allows the user to create / edit scripts and to define variables for the fields in the messages. The script uses pre-defined message templates to build call flow and perform send and receive actions. Script editor provides options to run the test for multiple iterations in sequential or random flow. Commands allow retransmission of messages with specific interval.
Command Line Interface
Supports scripting through a Command Line Interface (CLI) such as the Python, and TCL, using MAPS™ client-server functionality (requires additional license)
MAPS™ can be configured as server-side application, to enable remote controlling of the application through multiple command-line based clients. Supported clients include C++, TCL, Python and others. TCL provides a simple scripting language, with programming facilities such as looping, procedures, and variables. The TCL Client application includes a MapsTclIfc.dll file, a packaged library that enables communication with the Server from a TCL environment.
User can remotely perform all functions such as start test bed setup, load scripts and profiles, apply user events such as send digits/file/tones, detect digits/file/tones, dial, originate call, terminate call, start and stop traffic and so on. User can also generate and receive calls through commands. This client application is distributed along with MAPS™ Server application. Multiple MAPS™ CLI servers can be controlled remotely from single client application (such as TCL, Python, etc).
Call Statistics, Events, Link Status
Call Status & Message Statistics - By default, all call handling scripts (irrespective of the type of the functions) are assessed by MAPS™ to provide statistical information about Total Calls, Active Calls, Completed Calls, Passed Calls, Failed Calls, and Calls/Sec. It is also possible to categorize the statistical information as per the call handling scripts. In addition, Call Generation and Call Reception windows provide useful call status & script execution results.
In addition, Message Stats option for any specific protocol, logs number of times the messages are being transmitted (Tx Count) and received (Rx Count), thus allowing user to monitor the occurring events.
Events Reporting – MAPS™ provides Event Log, Error Events, and Captured Errors windows that log the captured events and errors encountered during the progress of the call.
Link Status - Link Status window indicates transport related information of the protocol, for example, if SCTP is used as transport, it indicates if the association is Up or Down in the Link Status window. MAPS™ IuCS ATM uses SSCOP transport and the associated link status is indicated as Up or Down in the Link Status window.
MAPS™ IUP Command Line Interface
A typical MAPS™ IUP command line interface consists of:
- A TCL interface communicating over TCP/IP to a Rack PC with T1/E1 Software
- The Rack PC consists of MAPS™ Client IFC, MAPS™ CLI Server, T1/E1 Software (including Windows Client Server software) and a Dual T1/E1 Card
- A patch panel for RJ-11 connections to the outside world
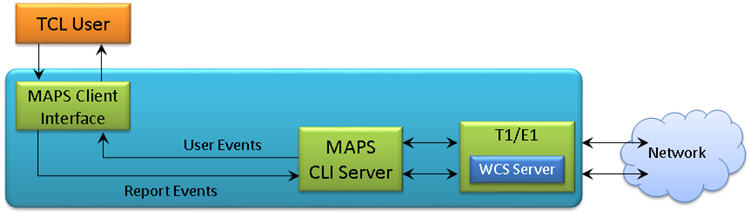
- TCL Client – Acts as User Interface, which executes TCL Scripts.
- MAPS TCL Interface (MAPS Client IFC) – acts as an interface between MAPS™ CLI Server and its client TCL. It interprets the TCL Commands and forms the appropriate command as understood by CLI Server and vice versa.
- MAPS™ CLI Server is an executable that inherits all features of MAPS™ without GUI. It listens to a TCP message socket to receive and execute commands from client and sends the responses back to client.
T1/E1 Windows Client Server (WCS) - Windows Client/Server software performs all IUP emulation primitives including signaling, tone detection, file transfer, tx/rx digits and other traffic functions.
TCL application consists of three functional modules: Tool Command Language (Tcl) Client and Script, MAPS™ Tcl Interface, and MAPS™ Server
In TDM CLI, MAPS™ Server constitutes two server modules, namely MAPS™ CLI server and GL WCS server.
- MAPS™ CLI Server
MAPS™ CLI Server is an executable which inherits all features of MAPS™ without the graphical user interface. Instead it listens to TCP message socket to receive and execute commands from the client and sends the responses back to the client.
- GL's Windows Client Server
GL's Windows Client/Server software allows the user of T1/E1 analysis cards the capability of remote operation, automation, and multi-site connectivity.
TCL client console displaying the Client interface started, Connection established, and handling IUP signaling and detect digits traffic at IUP Incoming Network side.
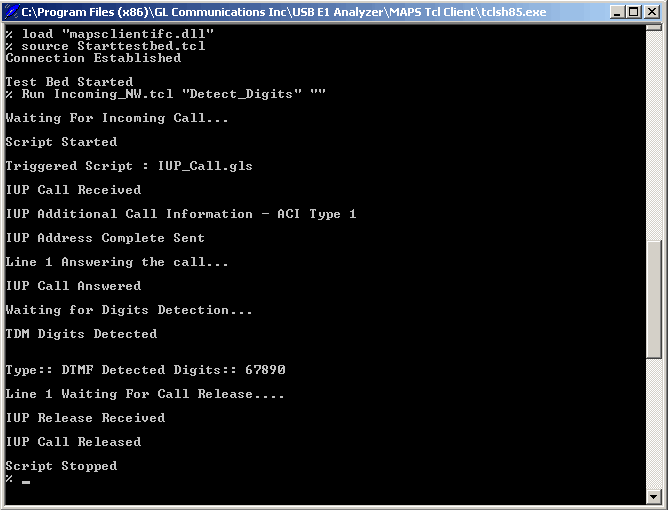 |
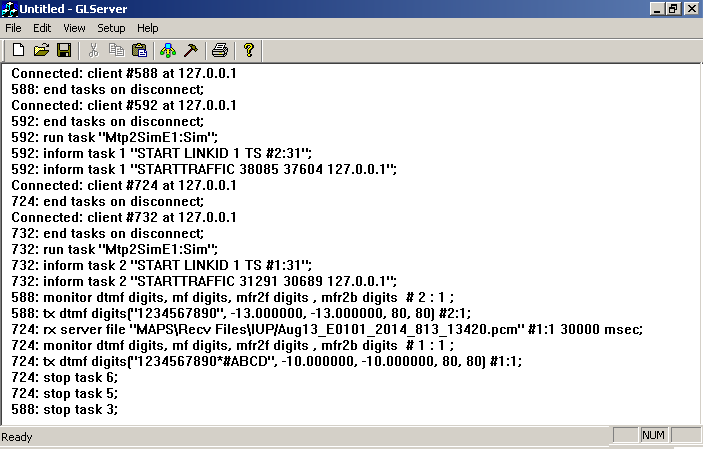 |
| TCL client at IUP Incoming Network side | WCS Server interfacing with the CLI Server |
Resources
Please Note: The XX in the Item No. refers to the hardware platform, listed at the bottom of the Buyer's Guide, which the software will be running on. Therefore, XX can either be ETA or EEA (Octal/Quad Boards), PTA or PEA (tProbe Units), XUT or XUE (Dual PCIe Express) depending upon the hardware.
| Item No. | MAPS™ for TDM Network (requires T1 or E1 Hardware and Basic Software) |
| XX682 | MAPS™ IUP Emulator |
| XX648 | MAPS™ ISDN Emulator |
| XX649 | MAPS™ SS7 Emulator |
| XX647 | MAPS™ SS7 Conformance |
| XX692 | MAPS™ GSM A Emulator |
| XX693 | MAPS™ GSM Abis Emulator |
| XX651 | MAPS™ CAS Emulator |
| XX652 | MAPS™ MC-MLPPP Conformance |
| XX694 | MAPS™ MAP Emulator |
| XX696 | MAPS™ CAP Emulator |
| XX656 | MAPS™ INAP Emulator |
| XX624 | MAPS™ FXO FXS Emulator (only for tProbe) |
| Related Hardware | |
|---|---|
| FTE001 ETE001 |
QuadXpress T1E1 Main Board (Quad Port– requires additional licenses) OctalXpress T1E1 Main Board plus Daughter Board (Octal Port– requires additional licenses) |
| PTE001 | tProbe™ Dual T1 E1 Laptop Analyzer with Basic Analyzer Software |
| XTE001 |
Dual T1 E1 Express (PCIe) Boards (requires additional licenses) |
| Item No. | MAPS™ for Wireless Network |
| Related Software | |
| PKS140 | MAPS™ LTE S1 Emulator |
| PKS142 | MAPS™ LTE eGTP (S3, S4, S5, S8, S10, S11 & S16) Emulator |
| PKS141 | MAPS™ LTE X2 AP Emulator |
| PKS146 | MAPS™ SGs Interface Emulation |
| PKS160 | MAPS™ UMTS IuCS IP Emulator MAPS™ UMTS IuH IP Emulator |
| PKS164 | MAPS™ UMTS IuPS Emulator |
| PKS166 | MAPS™ UMTS Gn Gp Emulator |
| LTS220 | MAPS UMTS IuCS ATM Emulator over OC-3 / STM-1 requires LTS214 + LightSpeed1000™ Hardware; optional LTS217 |
| LTS214 | OC-3 / STM-1 SSCOP Server |
| LTS320 | MAPS UMTS IuCS ATM Emulator over OC-12 / STM-4 requires LTS314 + LightSpeed1000™ Hardware; optional LTS317 |
| LTS314 | OC-12 / STM-4 SSCOP Server |
| PKS131 | MAPS™ Gb Emulator over IP for BSC & SGSN |
| Related Hardware | |
| LTS100 | Lightspeed1000™ - Dual OC-3/12 STM-1/4 PCIe Card |
| Item No. | MAPS™ for IP Network |
| PKS122 PKS123 |
MAPS™ MEGACO Emulator MAPS™ MEGACO Conformance Test Suite (Test Scripts) |
| PKS124 |
MAPS™ - MGCP Protocol Emulation with Conformance Test Suite |
| PKS120 PKS121 |
MAPS™ SIP Emulator SIP Conformance Test Suite (Test Scripts) |
| PKS126 | MAPS™ SIP I Emulator |
| PKS130 | MAPS™ SIGTRAN Emulator |
| PKS132 | MAPS™ MAP IP Emulator |
PKS147 |
MAPS™ Lb Interface Emulator |
PKS148 |
|
PKS153 |
MAPS™ IuPC Interface Emulator |
| PKS151 | MAPS™ CAMEL IP Emulator |
| PKS135 | MAPS™ ISDN SIGTRAN (ISDN IP) |
| PKS137 | MAPS™ GSM A IP Emulator |
| PKS155 | MAPS™ BICC IP Emulator |
| PKS136 | MAPS™ INAP Emulator (ANSI, ITU) |
| PKS139 | MAPS™ Diameter Emulator |
| Item No. | Traffic Options |
| XX610 XX620 XX646 |
File based Record/Playback Transmit/Detect digits (Place Call/ Answer Call) Multi-Channel TRAU Tx/Rx Emulation and Analysis |
| PKS102 | RTP Soft Core for RTP Traffic Generation |
| PKS200 | RTP Pass Through Fax Emulation |
| ETH100 ETH101 ETH102 ETH103 |
PacketCheck™ - Packet GTP Traffic Simulation Mobile Traffic Core-GTP Mobile Traffic Core-Gateway Mobile Traffic Core - GPRS Gb |
| LTS217 | OC-3 / STM-1 AAL2 Traffic Core |
| LTS317 | OC-12 / STM-4 AAL2 Traffic Core |
| Item No. | Related Software |
| XX120 | SS7 Analyzer Software |
| OLV120 | Offline/ Remote SS7 Analyzer Software |
| XX100 | ISDN Analyzer Software |
| OLV100 | Offline/ Remote ISDN Analyzer Software |
| XX150 | T1 or E1 Real-time GSM Protocol Analyzer |
| OLV150 | Offline T1 or E1 GSM Protocol Analyzer |
| XX165 | T1 or E1 Real-time UMTS Protocol Analyzer |
| PKS120 | MAPS™ SIP Emulator |
| PKV100 | PacketScan™ (Online and Offline) |
| PKB100 PKB105 |
RTP Toolbox™ G.168 Echo Canceller Test Compliance Suite |
| PKV105 | SIGTRAN Analyzer (requires PKV100) |
| PKV107 | LTE Real-time LTE Protocol Analyzer (Requires PKV100) |