MAPS™ SIP I Protocol Emulator
Simulate SIP signaling with encapsulated ITU/ANSI/ETSI ISUP messages
Brochure Request a Demo / QuoteBackground
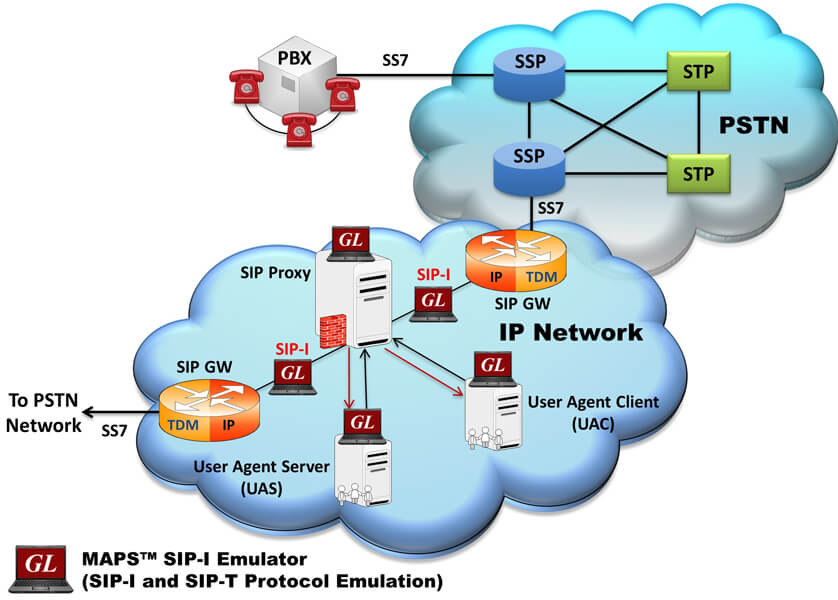
VoIP networks predominantly use SIP to setup and tear down voice calls and increasingly for video and multimedia calls. PSTN networks predominantly use SS7 to do the same. PSTN SS7 signaling is quite different from SIP signaling and in many cases PSTN SS7 signaling may be richer than SIP. There may be no one-to-one correspondence between SIP signaling messages and SS7 signaling messages. Also, it may not be possible to enhance SIP to accommodate the additional features of SS7, and vice-a-versa.
Another consideration, the mobile network is evolving to an all IP network; hence it is advantageous to transport voice using SIP with SS7 routing capabilities intact - thus the need for SIP to SS7 interworking. When a SIP-I is used to bridge the SS7 endpoints, the ISUP messages are carried (encapsulated) along with SIP signaling messages.
Overview
GL’s Message Automation & Protocol Simulation (MAPS™) is an advanced protocol simulator/tester traffic generator for SIP-ISUP simulation over IP. MAPS™ SIP I can simulate SIP-ISUP signaling specification as defined by the ITU / IETF standards ITU-T Q.1912.5.
MAPS™ product for SIP-I provides only the IP side of the Gateway at both ingress and/or egress depending on what one is trying to emulate. In general, MAPS™ is a powerful Protocol Test platform, supporting a wide range of protocols including TDM, IP, and Wireless infrastructure protocols.
MAPS™ SIP I is designed for SIP-I Testing can simulate Signaling Gateway / Softswitch as a User Agents Client (UAC), which sends SIP requests with ISUP message and User Agent Server (UAS), receiving and returning SIP responses with proper ISUP message attached.
MAPS™ SIP I (Item # PKS126)
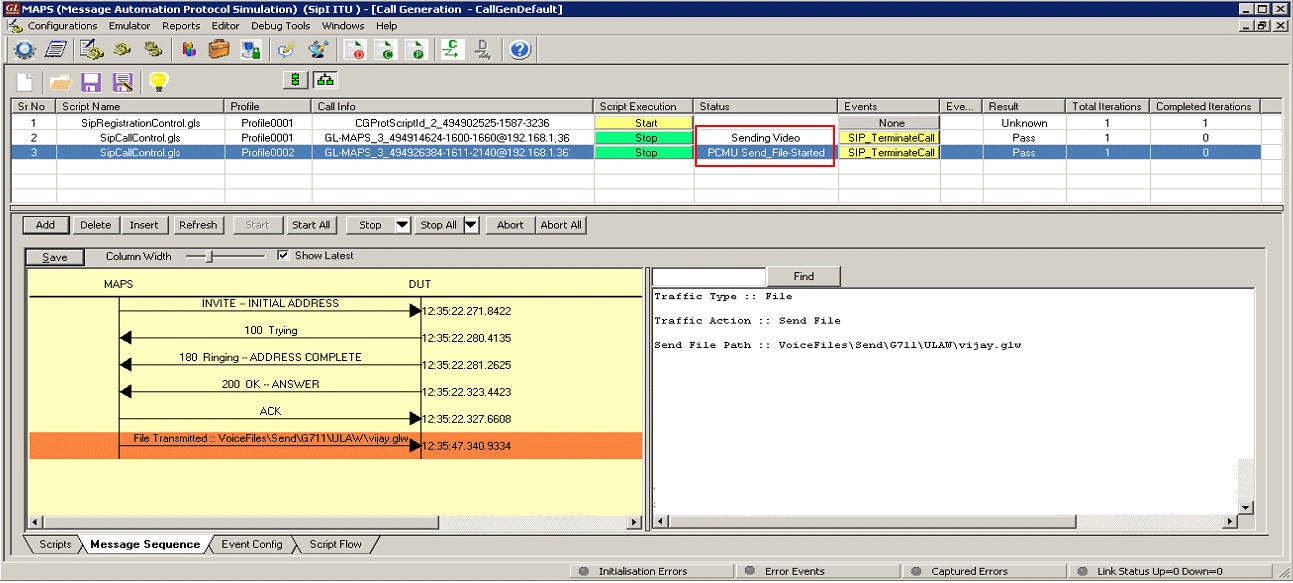
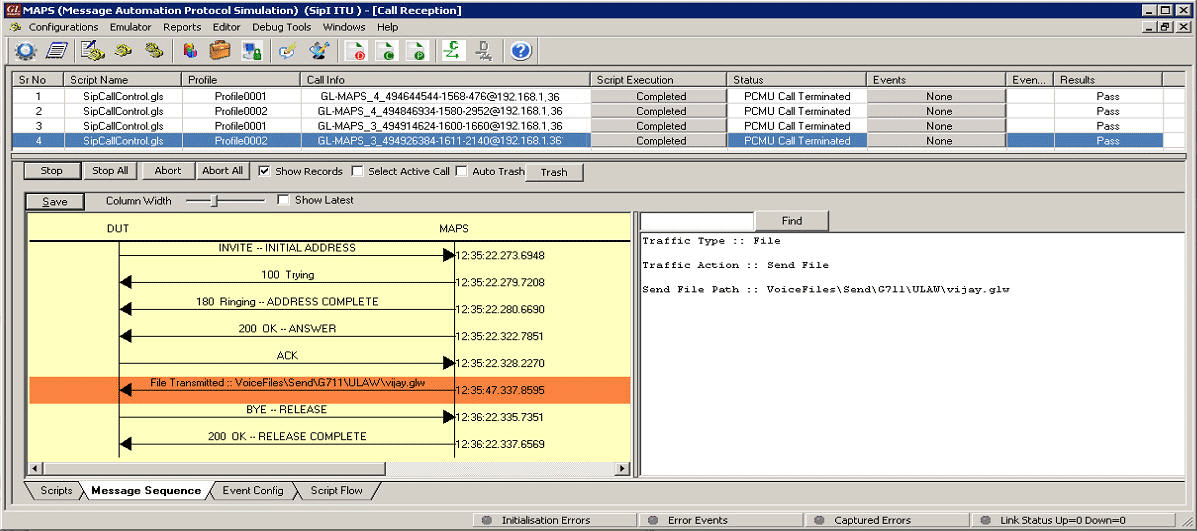
The MAPS™ SIP I supports powerful tools like Message Editor, Script Editor and Profile Editor which allow new scenarios to be created or existing scenarios to be modified using SIP-I messages and parameters. It gives the flexibility of modifying any message so that we can easily duplicate the messages generated by any entity to resolve interoperability issues.
With the purchase of RTP Core license (PKS102), MAPS™ SIP I supports transmission and detection of various RTP traffic such as, digits, voice file, single tone, dual tones, IVR, FAX*, and Video*. With regular RTP traffic, the maximum Simultaneous Calls up to 2500, and Calls per Second up to 250 is achievable. Almost all industry standard voice codec supported.
GL’s MAPS™ SIP I is also available in High Density version (requires a special purpose network appliance and PKS109 RTP HD licenses). This is capable of high call intensity (hundreds of calls/sec) and high volume of sustained calls (tens of thousands of simultaneous calls/platform).
** Some of these traffic types requires additional licenses – contact GL for more information
Also supports various traffic events simulation during the course of a call, which is listed below:
Signaling Events
- Answer Call - Used to Accept the Call from DUT
- Place Call - Places the Call to other End by initiating the Invite Message.
- Terminate - Terminates the call using BYE Method
RTP Traffic Events – digits, tones, files
- Send File, Receive File, Stop Send File
- Send Digits, Detect Digits, Stop Send Digits
- Send Test Tone, Detect Test Tone
- Send Tone, Detect Tone, Stop Send Tone
MAPS™ SIP-I also supports command line interface to remotely control MAPS™ from client environment. The MAPS™ APIs allows for programmatic and automated control over all MAPS™ platforms. Each MAPS™ server can receive multiple client connections (such as TCL, Python, VBScript, Java, or .Net) via APIs for complete automation.
GL also provides a Packet Analyzer for on-line capture and decode of the SIP signaling in real-time both during tests and as a stand-alone tracer for live systems.
Main Features
Signaling |
|
Traffic |
|
Other Features |
|
CLI |
|
Applications |
|
Supported Protocol Standards
| Supported Protocols | Specification Used |
|---|---|
| SIP-I (Profile-C) | ITU Q.1912.5 - Interworking between Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and ISDN User Part |
| SIP-T | IETF RFC 3372 |
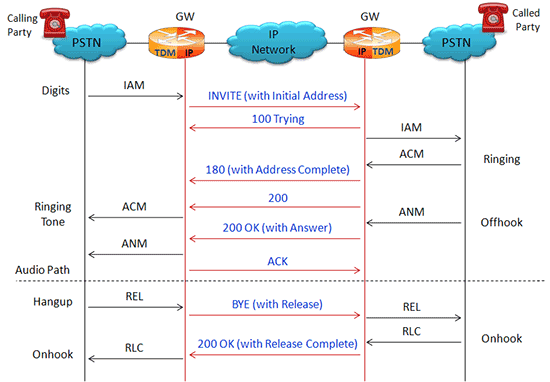
Typical SIP-I Procedure
As shown below, the ingress gateway, the IP Network, and egress gateway provide a bridge for the SS7 signaling and traffic. SIP-I provides a framework for the integration of ISUP with SIP. The ingress and egress gateways, at the point of interconnection provide the SS7 ISUP message encapsulation and vice-versa. RTP is used to carry voice traffic as usual within the SIP network from gateway-to-gateway.
SIP-I Typical Call Flow
Secure RTP (SRTP) Traffic Simulation
MAPS™ SIP-I supports Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (or SRTP) traffic initialized over TLS (Transport Layer Security) Transport / SSL (OpenSSL) with a Certificate and Key. SIP-I is a signaling protocol, and carries traffic (voice, digits, tone, IVR, FAX, data) using RTP. To Secure traffic communication between the Client-server, MAPS™ application uses the TLS protocol across a network, adding SRTP (secure RTP) to encrypt the actual media portion of the calls preventing eavesdropping and tampering.
Secured communication uses cryptographic protocols - Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), both are referred as 'SSL'.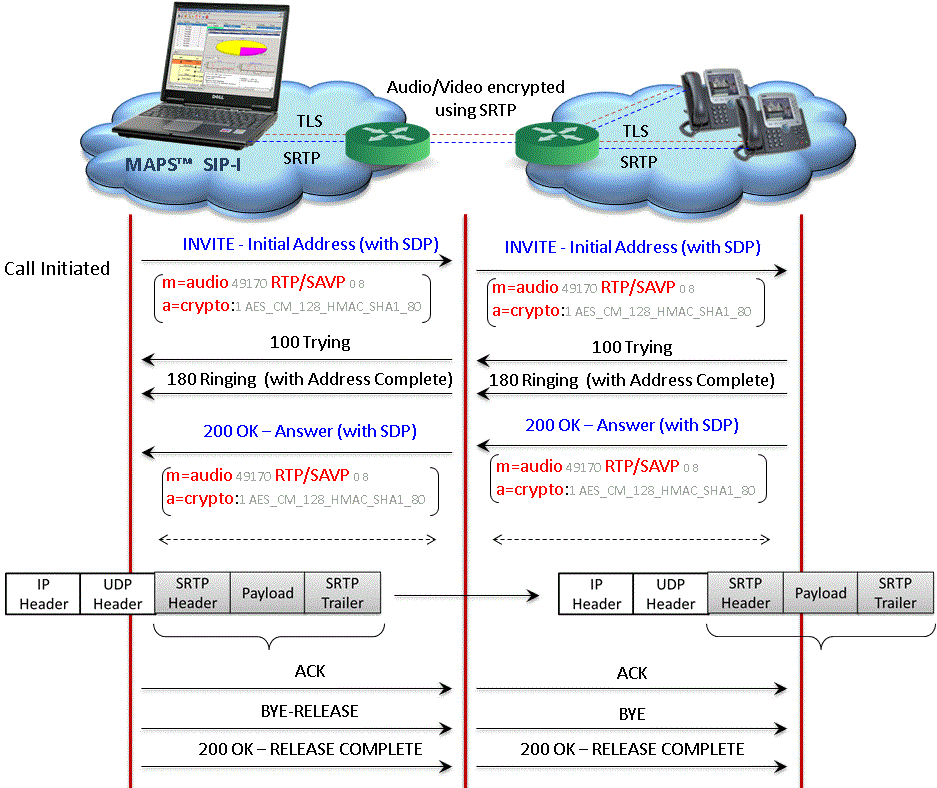
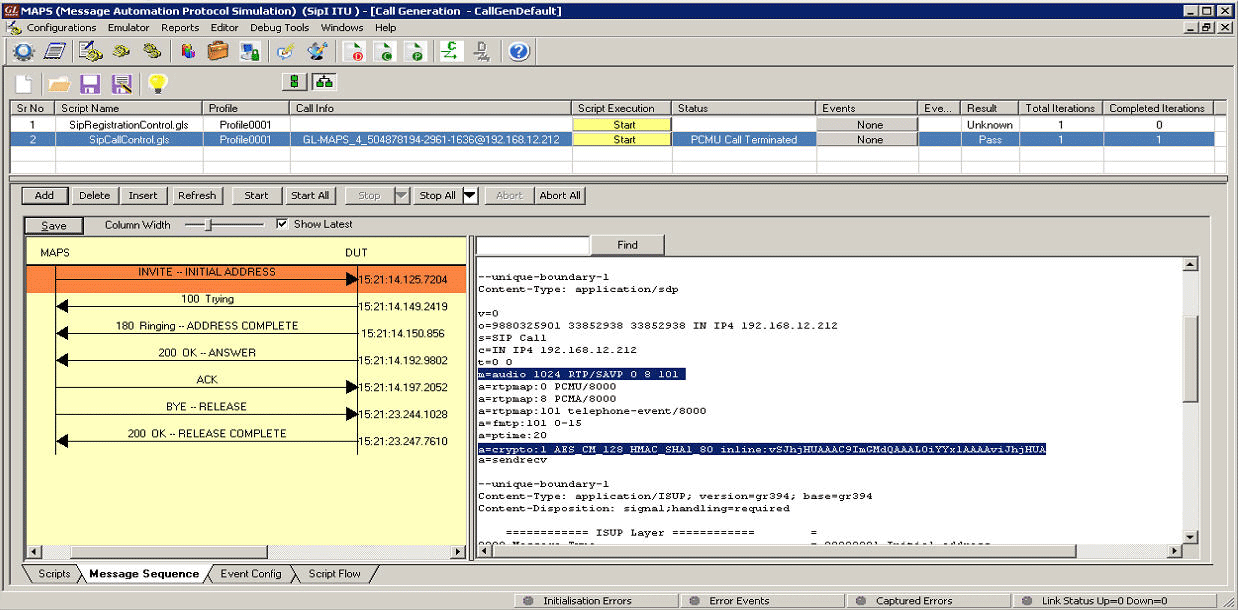 SRTP Audio Call Generation |
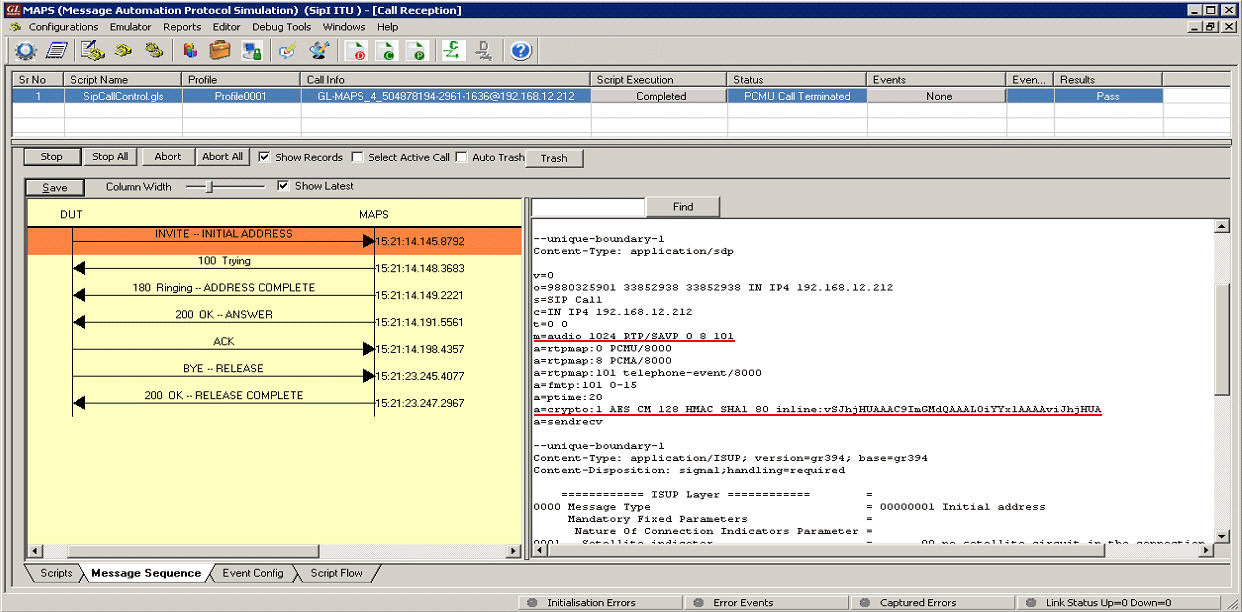 SRTP Audio Call Reception |
Resources
Please Note: The XX in the Item No. refers to the hardware platform, listed at the bottom of the Buyer's Guide, which the software will be running on. Therefore, XX can either be ETA or EEA (Octal/Quad Boards), PTA or PEA (tProbe Units), XUT or XUE (Dual PCIe Express) depending upon the hardware.
| Item No. | MAPS™ SIP-I Protocol Emulation |
PKS126 |
MAPS™ SIP I Emulator |
PKS120 |
MAPS™ SIP Emulator |
| Brochure |
|---|
| MAPS™ SIP I - Brochure |
| Presentation |
|---|
| MAPS™ SIP I - Presentation |