MAPS™ LTE SLs Emulator
Simulation of SLs interface between "Enhanced Serving Mobile Location Center" and "Mobile Management Entity" using Location Services Application Protocol (LCS-AP) supporting "Location Services".
Brochure Request a QuoteBackground
Accurate location services find its use in many public operations such as emergency services, vehicle tracking, stolen assets tracking, advertising, and social networking. Location Service is used to estimate the geographic location of a Mobile Station (MS) and/or valid Mobile Equipment (ME), expressed in latitude and longitude, represented in a well-defined universal format. Location Services (LCS) architecture follows a client/server model with a positioning node acting as the server providing information to external LSC clients.
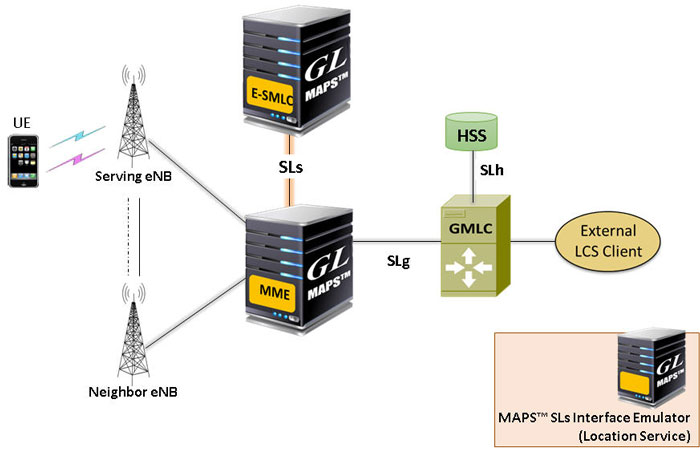
In the LCS network, GMLC (Gateway Mobile Location Center) is the positioning node and center point of the architecture that holds the position information by communicating with other network elements within the network. All LCS clients communicates with this node to request positioning information.
The LCS architecture in LTE is similar to GSM/UMTS network and supports the following interfaces for accommodating location services–
- SLs interface - MME is accessible to the E-SMLC via the SLs interface using LCS-AP protocol
- SLg interface - MME is accessible to the GMLC via the SLg interface using Diameter protocol
- SLh interface - HSS is accessible to the GMLC via the SLh interface using Diameter protocol
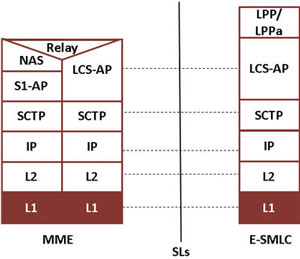
LCS Application Protocol (LCS-AP) supports the location services over SCTP in E-UTRAN. The LCS-AP message set is applicable to the SLs interface between the E-SMLC and the MME. The SLs interface is used to convey LCS-AP messages and parameters between the MME to the E-SMLC. It is also used for tunnelling LTE Positioning Protocols (LPP between the E-SMLC and the target UE, LPPa between the E-SMLC and the eNB), which are transparent to the MME as described in 3GPP TS 36.305.
Overview
Message Automation and Protocol Simulation (MAPS™) is GL’s general purpose platform for emulation of communication protocols. MAPS™ SLs interface emulator is designed to simulate SLs interface between E-SMLC (Enhanced Serving Mobile Location Center) and MME (Mobile Management Entity) supporting Location Services (LCS), as defined in 3GPP TS 29.171 specifications.
The application is available as
- MAPS™ SLs (Item # PKS148) for SLs interface in LCS network.
The figure above shows the architecture applicable to the positioning of a UE with E-UTRAN access. The SLs interface is used to convey LCS-AP (LCS Application Protocol) messages and parameters between the MME to the E-SMLC. It is also used for tunnelling LTE Positioning Protocols (LPP between the E-SMLC and the target UE), which is transparent to the MME as described in 3GPP TS 36.305.
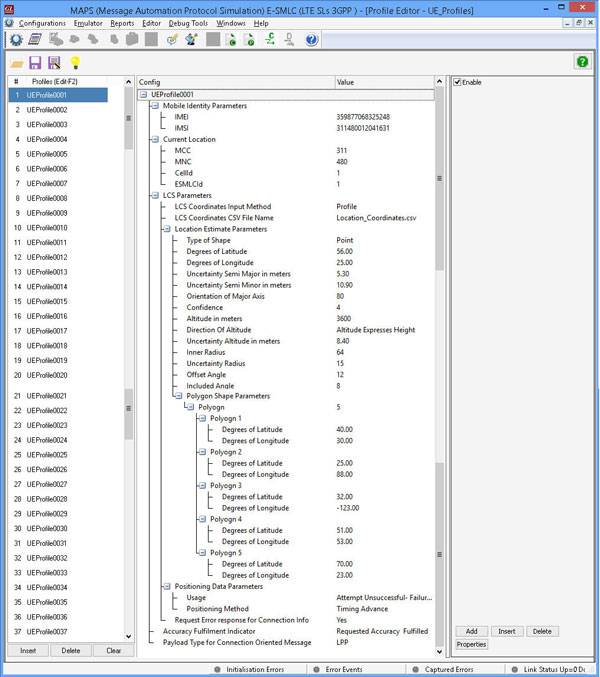
MAPS™ SLs emulator supports LCS AP protocol messages and LPP payload protocols required for simulating E-SMLC and MME network elements over SLs interface. MAPS™ SLs emulator supports UE based positioning method (A-GNSS) in LTE network.
MAPS™ SLs emulator supports simulation of location service procedures between E-SMLC and MME using UE based A-GNSS positioning method, thus testing either or both entities for all probable scenarios.
MAPS™ E-SMLC seamlessly interacted with customer’s real-time MME requesting the current location of a subscriber by initiating LPP location requests on LCSAP sessions.
MAPS™ SLs supports following LCS-AP and LPP procedures:
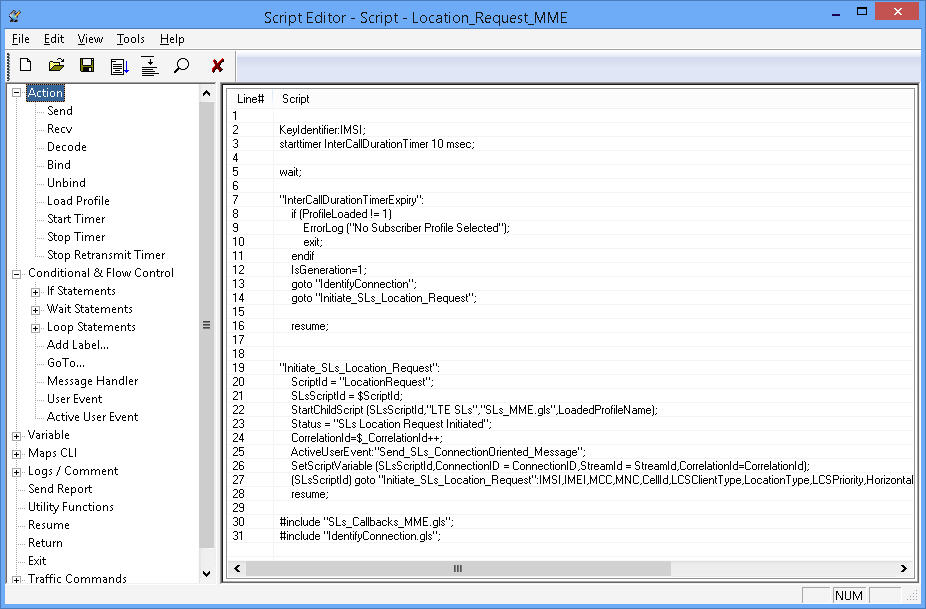
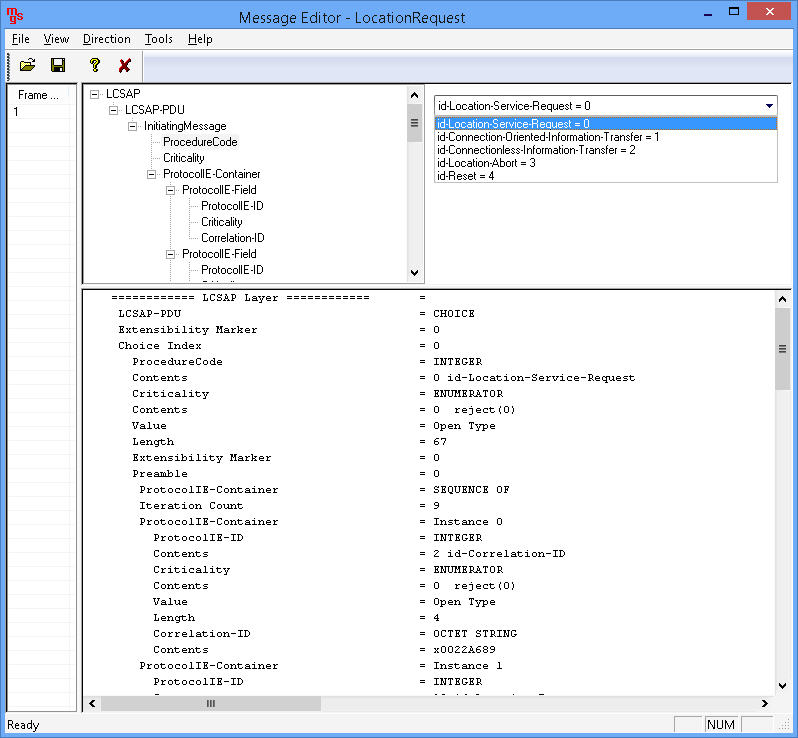
- Location Service Request - The MME sends an LCS-AP Location Request message to the E-SMLC associated with the current serving cell for the target UE to obtain the location estimate for a target UE in E-UTRAN.
- Location Information Exchange - purpose is two-way transfer of LPP messages between an E-SMLC and a MME. E-SMLC and a MME. Following are the supported LPP procedures:
- Request Capabilities (E-SMLC à UE)
- Provide Capabilities (UE à E-SMLC)
- Request Location Information (E-SMLC à UE)
- Provide Location Information (UE à E-SMLC)
- LPP Abort
- LPP Error
- LPP ack
- Location Abort procedure - procedure is used by one endpoint to notify the other endpoints to abort an ongoing procedure.
- Reset procedure - procedure enables an E-SMLC or an MME that has undergone a failure with loss of location service transactions to indicate this to a partner entity. The recipient entity can then release its own connection and transaction resources.
MAPS™ also supports simulation of other entities and interfaces indicated in Location Services architecture with the following MAPS™ suite for LCS - MAPS™ SLh between GMLC and HSS, MAPS™ SLg between GMLC and MME, MAPS™ Lg between GMLC and MSC, MAPS™ Lh between GMLC and HLR, and MAPS™ Lb between BSC and SMLC.
Main Features
- Useful tool to simulate Location services procedures over SLs interface
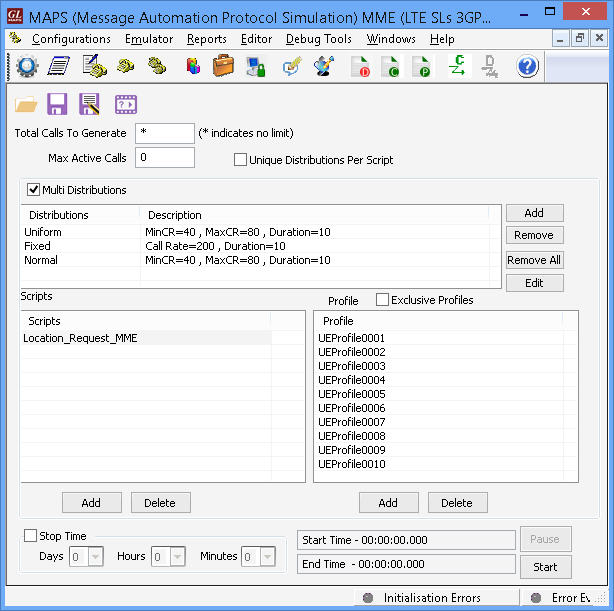
- Emulator can be configured as MME, E-SMLC nodes and study the call flow and exchange of signaling messages between any of these nodes
- User-friendly GUI for generating hundreds of UE Signaling (Load Testing) over SCTP transport.
- Ready scripts for LCS-AP procedures –
- Location Service Request
- Location Information Exchange LPP procedure
- Request Capabilities (E-SMLC → UE)
- Provide Capabilities (UE → E-SMLC)
- Request Location Information (E-SMLC → UE)
- Provide Location Information (UE → E-SMLC)
- LPP Abort
- LPP Error
- Location Abort procedure
- Reset procedure
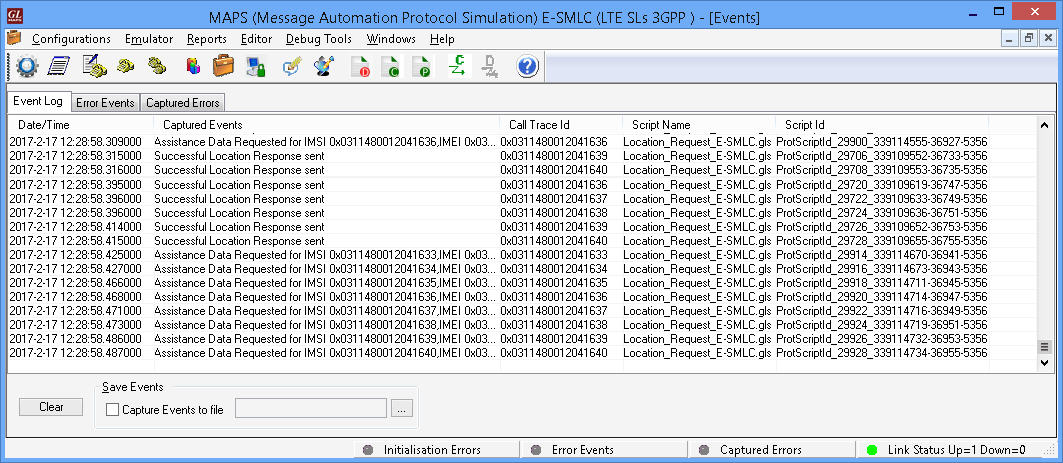
- Provides protocol trace with full message decoding of the LCS-AP and LPP messages.
Supported Protocols Standards
SLs Interface Procedures
The SLs interface procedures can be divided as follows:
- Location service request procedure
- Location information exchange LPP procedures
- Request Capabilities (E-SMLC → UE)
- Provide Capabilities (UE → E-SMLC)
- Request Location Information (E-SMLC → UE)
- Provide Location Information (UE → E-SMLC)
- LPP Abort
- LPP Error
- LPP ack
- Location Abort procedure
- Reset procedure
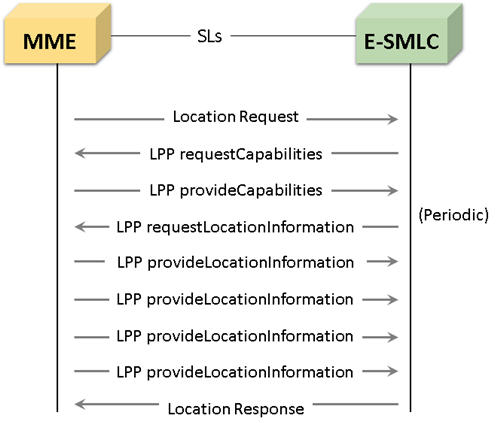
Location Service Request and Information Exchange LPP Procedures
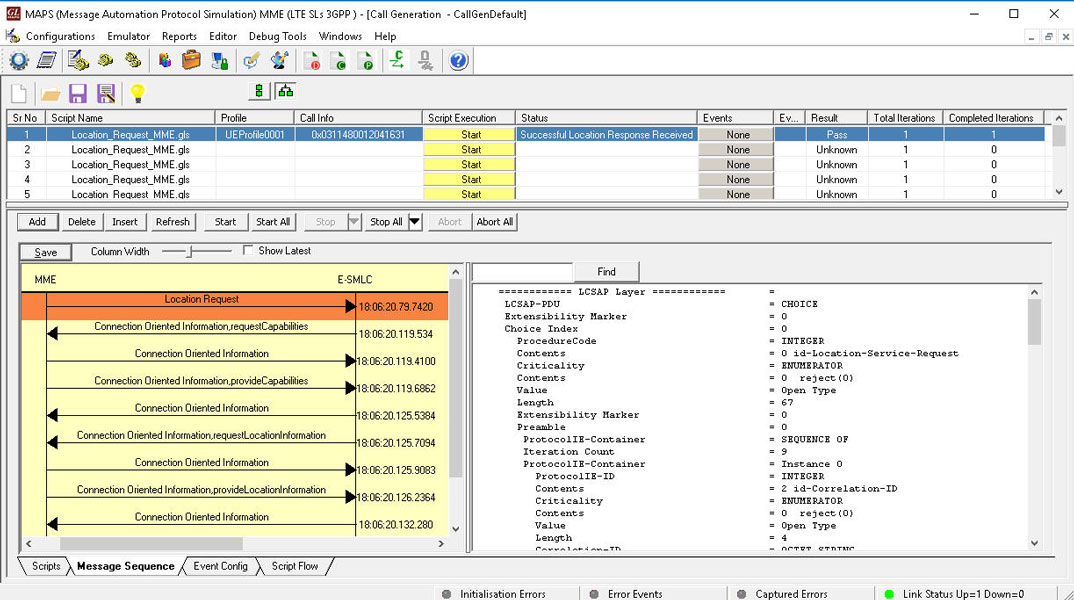
The following illustrates the location service request and information exchange LPP procedures over LCS based SLs interface:
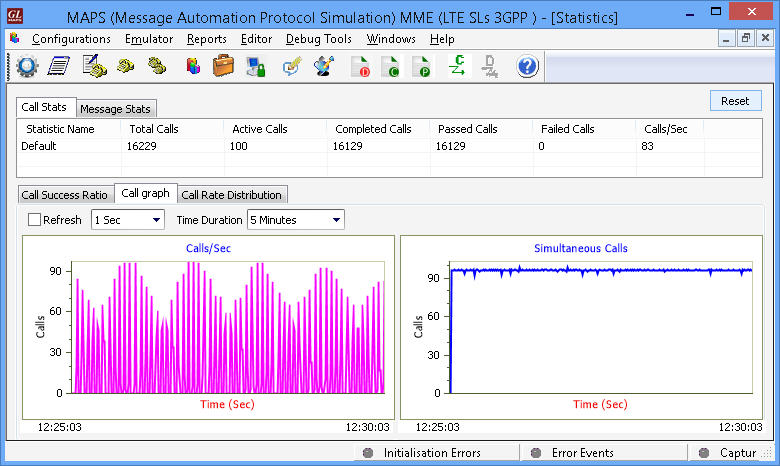
MAPS™ SLs interface emulator can be configured as MME (Mobility Management Entity) initiating the procedure by transferring LTE Positioning Protocol (LPP) messages to E-SMLC (Enhanced Serving Mobile Location Center) while a location request procedure for the target UE is ongoing.
MAPS™ SLs simulating as MME node
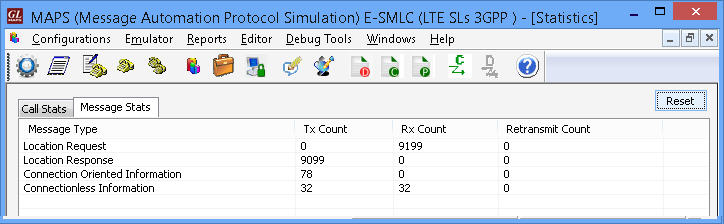
On receiving Location request, MAPS™ E-SMLC will send LPP Request capabilities message to UE via MME (transparent to MME) to get the positioning methods (AGNSS) UE supports. E-SMLC will then extract all the location estimation parameters from the received message and send the LCSAP location Response to MME.
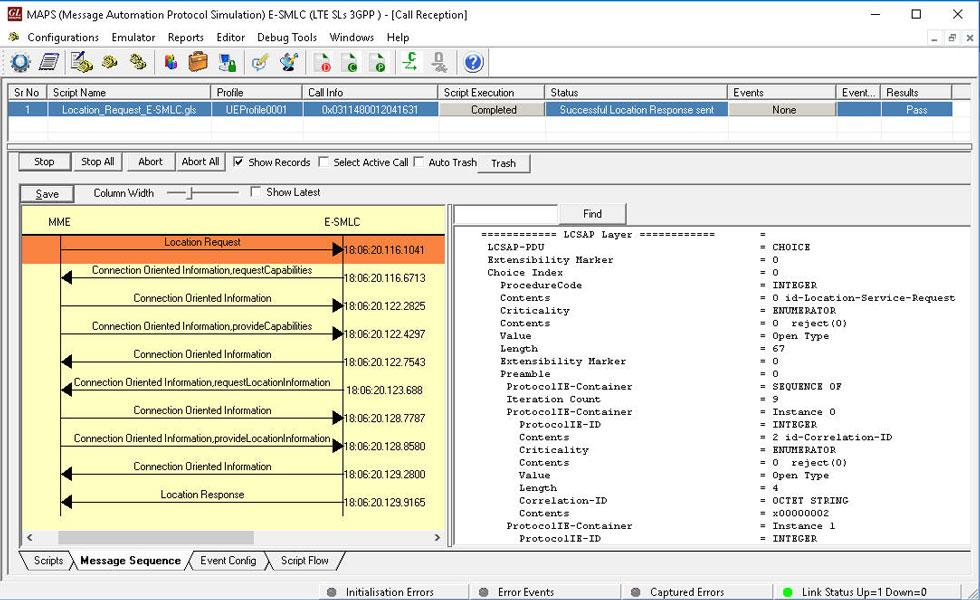
MAPS™ SLs simulating as E-SMLC node
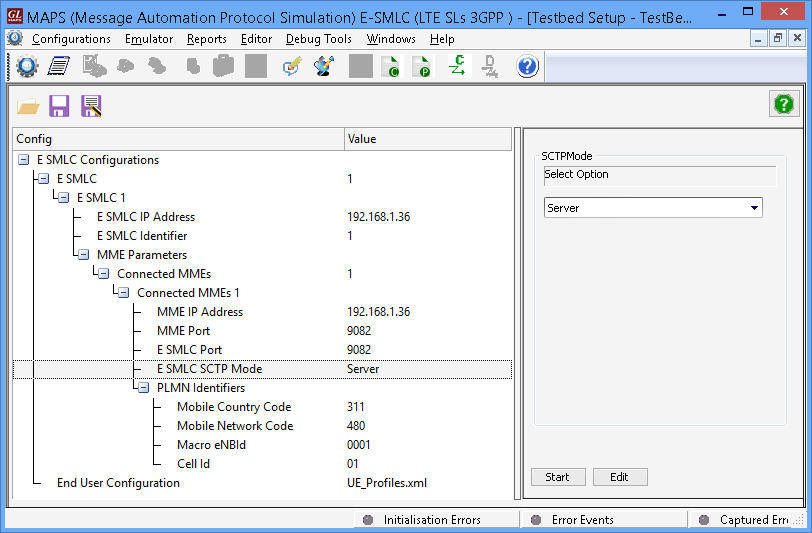
Screenshots
Resources
Please Note: The XX in the Item No. refers to the hardware platform, listed at the bottom of the Buyer's Guide, which the software will be running on. Therefore, XX can either be ETA or EEA (Octal/Quad Boards), PTA or PEA (tProbe Units), XUT or XUE (Dual PCIe Express) depending upon the hardware.
| Item | Description |
| PKS148 | MAPS™ SLs (LCS-AP) Interface Emulator |