GL Communications Inc’s Advanced Automated Voice Quality Testing Solution
Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA - May 15, 2023 - GL Communications Inc., a global leader in telecom test and measurement solutions, addressed the press regarding their latest automated Voice Quality Testing (VQT) solution - AutoVQT™. With this advanced solution, users can now analyze thousands of audio files in just few minutes, providing quick and accurate voice quality testing results.
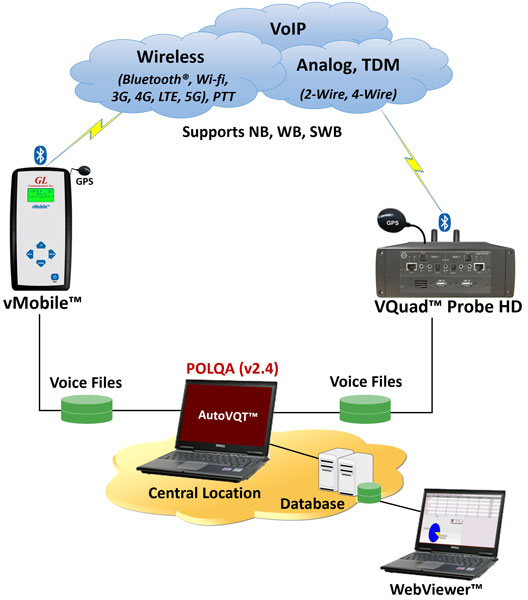
Overview
“GL's AutoVQT™ is an advanced, automated solution that analyzes thousands of voice files in mere minutes, effectively evaluating the quality of voice communications across various networks including VoIP, Mobile, and PSTN. This solution utilizes the Perceptual Objective Listening Quality Assessment (POLQA per ITU-T P.863 version 2.4) algorithm, which is widely acknowledged as the industry benchmark for assessing voice quality to deliver highly accurate and reliable results, ensuring that voice quality testing is precise and up to industry standards”, said Robert Bichefsky, Director of Engineering at GL Communications Inc.
The AutoVQT™ application works in conjunction with GL's voice and data testing solution- VQuad™, portable handheld voice and data solution - vMobile™, GL Message Automation and Protocol Simulation (MAPS™), and T1/E1 Analysis platforms reducing analysis time and increasing efficiency. With the Voice Quality server software installed on Windows® PC and client software running on Windows®/Linux® platforms, users can analyze large quantities of PCM files obtained from any network as well as different sampling rates in minutes, significantly reducing the time required for analysis.
The AutoVQT™ fully supports analysis using POLQA ITU version 2.4 algorithm for Narrowband (NB 8000 sampling), Wideband (WB 16000 sampling), and Super Wideband (SWB 48000 sampling). The tool offers a user-friendly interface for automatic operation and generates comprehensive reports that provide detailed information on voice quality metrics such as Mean Opinion Score (MOS), Delay, Jitter, Packet Loss and more. These reports help users to identify issues and make data-driven decisions to improve voice quality. The tool supports a wide range of codecs, including G.711, G.722, AMR, and EVS, making it suitable for testing various types of voice communication.
The AutoVQT™ application operates automatically by applying the POLQA algorithm to degraded (recorded) audio files located within a user-specified local directory. Once the application detects a PCM (or WAV) voice file in the configured directory, the application automatically applies the required algorithm against the reference and degraded PCM voice files and generates the POLQA MOS. The application sends the POLQA results to the centralized database system - Webviewer™ which can filter, query, and generate custom reports.
Key Features
- Analyze thousands of bulk PCM voice files in mere minutes
- The Auto Test feature allows immediate analysis of files according to the configured settings upon invocation of the application
- Uses POLQA version 2.4 (ITU-T P.863) algorithm for voice quality testing supporting NB (8000 samples), WB (16000 samples) and SWB (48000 samples)
- AutoVQT™ analysis results include:
- POLQA MOS
- E-Model R-Factor
- Signal Level
- Noise Level
- Delay (requires simultaneous Send and Record of the voice files)
- Jitter
- Clipping
- Offers automatic mode of operation with centralized data access
- Supports voice quality testing over all types of telecom networks - Wireless, VoIP, TDM, and PSTN
- As part of the POLQA algorithm, the POLQA MOS is generated by utilizing the impact of Packet Jitter and Codec compression in VoIP and Wireless networks
- Provides remote monitoring with result query and real-time statistics using web based WebViewer™
- Enables real-time mapping of results directly on Google Maps when used in conjunction with VQuad™ or vMobile™ with GPS option and results sent to WebViewer™ central database
- Supports Application Programming Interfaces to enable the remote control of AutoVQT™ nodes
 Back to Press Releases Index Page
Back to Press Releases Index Page