Testing Voice Features in Legacy &
Next Generation Networks (NGN)
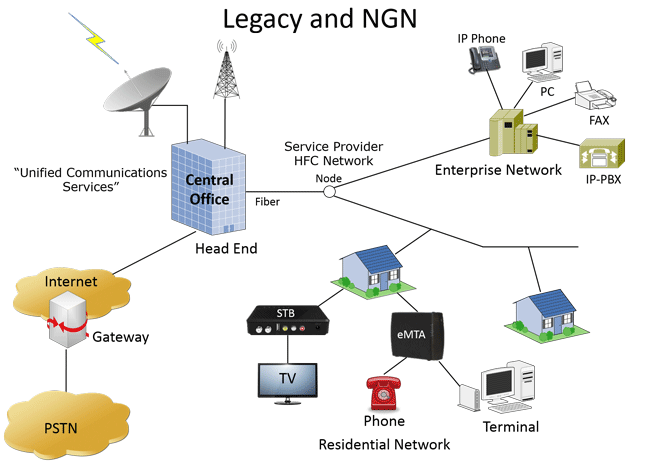
Next Generation Networks (NGNs) are based on broadband IP technology and are frequently promoted as "triple play" services, especially for residential to include voice, TV, and Internet.
In the enterprise case, the common conduit for voice, data, and video is Ethernet with Internet Protocol (IP) for transport and signaling. Voice will use SIP phones and IP PBXs or Hosted IP PBXs in the Cloud. This architecture will evolve to fully integrate with the desktop and converge Email, SMS, IM, Voice, and other services. Such NGNs freely offer advanced voice features that cost extra when provided by legacy circuit switched PSTN landlines.
NGN advanced voice features are similar to but more sophisticated than CLASS (Custom Local Area Signaling Service) features PSTNs offer. These features include three way calling, call waiting, call hold, caller id, call waiting with caller id among others. In many cases, these features involve detection and generation of tones and dual tones with varying cadences. Capability for testing higher quality voice (any codec support), inband and out-of-band digit transmission, and DSP are just some necessary functions of a test tool used for testing NGNs.
Testing such features cannot be performed with generic Bulk Call Generators / Receivers. In fact, signal processing functions are required to fully test these features, see Table 1. Common 2-Wire Signaling for NGN Voice Features. In the future, the residence architecture for voice is more likely to be 4 wire SIP based WiFi phones or 3G/4G phones with higher quality audio. In either case, voice features testing is extremely important.
To easily test NGN voice features, in both residence and enterprise, GL has introduced a library of functional capabilities within its standard emulation software platform called MAPS™, or Message Automation and Protocol Simulation. MAPS™ is a versatile telecommunications protocol emulator. MAPS™ APS and MAPS™ SIP are the specific MAPS™ products that provide functional capabilities to test and verify voice features of NGNs. In addition to these, GL’s voice, video, and data quality probe, VQuad™ Probe, extends the ability to perform detail QoS measurements and reporting. This hardware supports multiple physical interfaces for connecting to practically any wired or wireless network while automatically performing voice, video, and data testing.
All of the test tools mentioned above, can be easily integrated with "drag and drop" tools such as TestShell or scripting languages such as TCL, or with other scripting languages such as Python, TCL, VBA, Java™. One can create compliance test cases to perform simple to complex voice features testing on their network environment.
Listed below are some of the GL test platform variants widely accepted in the industry for testing voice, and data features –
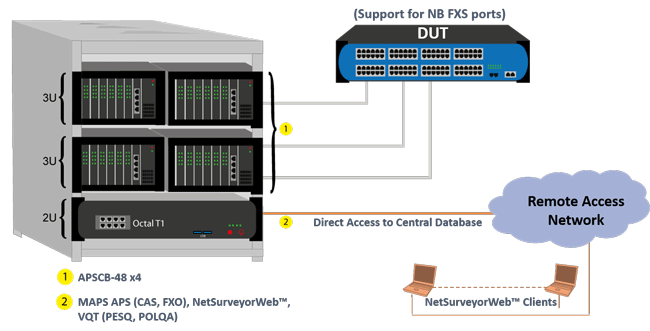
GL MAPS™ APS solution is capable of simulating up to 384 FXO NB (narrowband) ports. Shown in the figure below is a MAPS™ APS 192 port system configuration.
Similarly, GL’s VQuad™ FXO Probe solution is capable of simulating up to 24 Narrowband or Wideband FXO ports per probe. Shown in the figure below is a VQuad™ 24 port WB FXO Probe configuration.
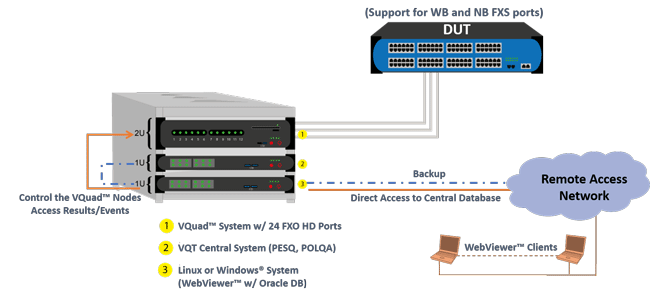
The above depicted systems supports all the below FXO features including support for both Narrow Band (NB) and Wideband (WB) Codec
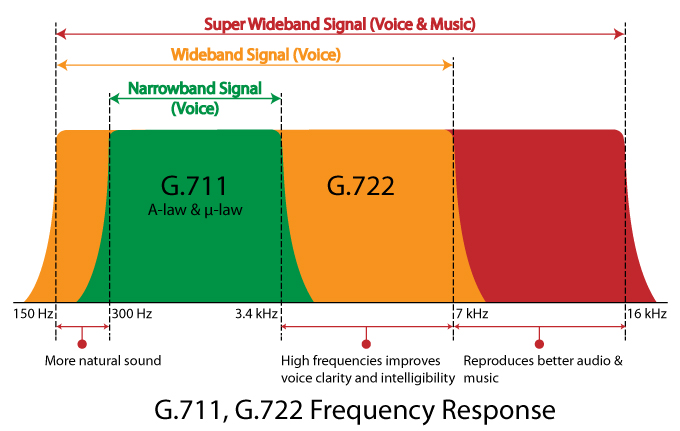
Table 1. Common 2-Wire and VoIP Signaling Requirements for NGN Voice, and Data Features
Standard manual and bulk call generation
Fax Feature Testing capabilities include -
|
Voice Feature Testing capabilities include -
Send or Detect
|
 Back to Complete Voice Quality Testing Solutions Index Page
Back to Complete Voice Quality Testing Solutions Index Page