Enhanced MAPS™ SIP to Support
Speech to text Interactive Voice Response
Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA – Aug 13, 2020 - GL Communications Inc., a global leader in telecom test and measurement solutions, addressed the press regarding their enhanced MAPS™ SIP Protocol Emulator version 20.6.10 to support Interactive Voice Response (IVR) testing that recognizes and responds to voice prompts using DTMF digits or voice, allowing automated IVR traversal and testing.
This newer version also includes enhancements for SIP signaling features, improvement in SIP load capability and a new feature to control the MSRP message generation rate over the SIP Calls.
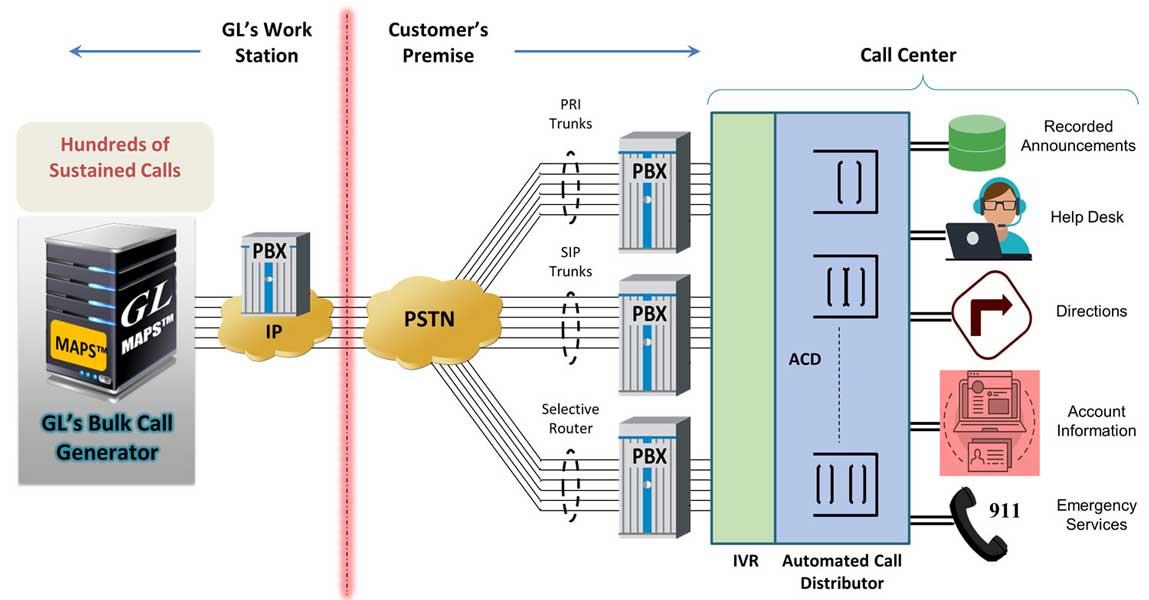
“GL’s MAPS™ SIP with GL’s Speech Transcription Server provides automated IVR testing by using speech to text to navigate through an IVR tree. IVR prompts are recorded by MAPS™ SIP and transcribed by the Speech Transcription Server. Transcribed text is compared to an expected text at each IVR stage to confirm the prompt”, said Vijay Kulkarni, CEO of GL Communications.
He further added, “once the IVR prompt is confirmed, MAPS™ sends DTMF or voice-based responses to move to the next stage. The expected IVR prompts and responses are defined by the customer to ensure completely customizable tests that are suitable for all IVR systems”.
“MAPS™ provides the necessary base to emulate different IVR call flows with complete automation. IVR tests start automatically once the call is established”.
Other enhancements include:
- MAPS™ SIP HD is enhanced to achieve up to 32K simultaneous SIP calls with duplex traffic per appliance (with 4x1Gbps NIC).
- For Instant Messaging (IM) calls, user can configure MSRP message rate distribution (number of messages per second) for specified load distribution duration uniquely for every MSRP session.
- Enhanced to support Attended Call Transfer feature as listed in RFC 5359 SIP service examples.
- Ability to support in-dialog and out-of-dialog transactions for UPDATE, SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, OPTIONS, REFER and INFO SIP methods.
- Supports usage of UPDATE SIP method for modifying the session parameters of early or confirmed SIP sessions.
 Back to Press Releases Index Page
Back to Press Releases Index Page