T1/E1 Power Spectral Display
Rx Signal Monitoring applications are now included with T1E1 Basic Software
Overview
The data received on a specified timeslot can be viewed in the spectral domain (spectral amplitude Vs frequency). A Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is applied to successive sample sets of the incoming data and displayed graphically. Adjust the frequency resolution by the FFT length (from 32 points to 8192 points). The data can be smoothed to lessen the effects of truncation by applying Hamming, Hanning, Harris, Blackman, Triangular, or Rectangular filter windows.
In addition to power spectrum display of the incoming signal, the following computations are provided:
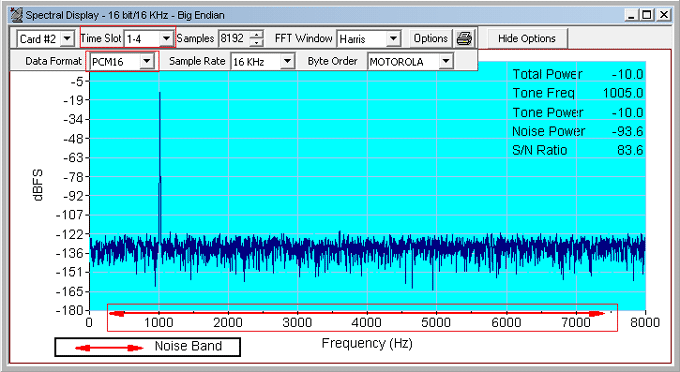
- Signal-to-noise ratio for the highest single frequency tone. The noise band can be adjusted to any range within the voice band
- Total noise power
- Tone power
- Tone frequency
- Total power
Description
Display Control:
The graphical display in Power Spectral Display can be magnified and moved by changing the Sample size depending on the maximum and minimum limits.
Card #:
Select the card, if operating with more than one card.
Time Slot:
Select the timeslot to be monitored here. You can use the spin control to advance through the timeslots, or key in the desired time slot directly.
Samples:
The sample size upon which the FFT is computed can be adjusted from 32 samples to 8192 samples. The rendering improves in accuracy as the sample size is increased, at the expense of losing responsiveness to rapidly changing signals.
FFT Window:
The following smoothing filters are provided: Blackman, Hamming, Hanning, Harris, Rectangular, and Triangular.
Decode Option
Decode options displays options to select Data Formats, Sample Rates, and Byte Orders.
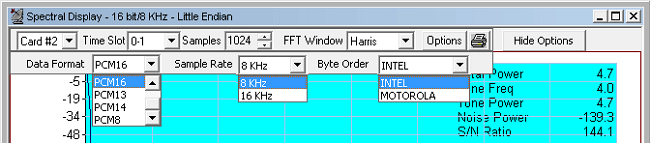
Data Format:
- aLAW: Default for T1 analyzer
- muLAW: Default for E1 analyzer
- PCM16: For 16-bit 8KHz signals, two consecutive timeslots are used. The byte order in which the two bytes of 16-bit data is determined by the selection of INTEL or MOTOROLA byte order options. Similarly, For 16-bit linear, 16 KHz signals, four consecutive timeslots are used. The lower-numbered timeslot pair carries the earlier 16-bit sample point in time, while the higher-numbered timeslot pair carries the later 16-bit sample point in time. The byte order is determined by the selection of INTEL or MOTOROLA options. The four timeslots, when used this fashion, make up a four-byte hyperchannel
- PCM13: Displays 13 bit data on two selected timeslots for 8KHz sample rate. Byte order is determined by the selection of INTEL or MOTOROLA options
- PCM14: Displays 14 bit data on two selected timeslots for 8KHz sample rate. Byte order is determined by the selection of INTEL or MOTOROLA options
- PCM8: Displays raw data on single timeslot without any decoding
- Sample Rate: Sample rate option is available only for PCM16 data format. 8KHz and 16KHz sample rate options are available
- Byte Order: Provides INTEL or MOTOROLA byte order options
- INTEL (Little Endian): The lower-numbered timeslot carries the least-significant byte (LSB), while the higher-numbered timeslot carries the most-significant byte (MSB)
- MOTOROLA (Big Endian): The lower-numbered timeslot carries most-significant byte (MSB), while the higher-numbered timeslot carries the least-significant byte (LSB)
- Hide Option: Click on Hide Options button to hide Decode Options
Options:
Click Options, a drop-down menu appears. The various options are:
Normal Display:
Selecting this option causes the frequency spectrum of the incoming signal to be repeatedly calculated, and displays the calculated spectrum by updating.
Averaging Display:
Selecting this option opens up the Spectrum Averaging dialog box. In this dialog, specify how the average is to be calculated. Once you have specified a value, the display is averaged over time in accordance with the parameters provided.
Peak Hold Display:
Selecting this option will retain the max peak value of the samples plotted.
Parameters:
Selecting this option opens up the Graph Parameters dialog, which allows you to control certain aspects of the graphic display such as its position, background color, and border attributes as shown in figure.
Grid Lines:
Selecting this option toggles the appearance of grid lines on the display. When checked, the grid lines appear in the graphic portion of the display. When unchecked, grid lines are not displayed.
-
Noise Band:
Selecting this option opens up the Noise Band Range dialog box. Noise band is defined as the range of frequencies over which the power is calculated to determine noise power and the signal-to-noise ratio. The default frequency is 300 Hz to 3400 Hz.
Refresh Legends:
This option is useful if the Legends (power and frequency measurement labels) have been over written by the graphic display.
- Print Page option is to print the Power Spectral Display window on the current selected printer
- Print Graph option is to print the graphic portion of the Power Spectral Display on the current selected printer
- Printer Setup option is to show the standard Windows Printer Setup dialog
- Printing Options is to show the Print Parameters dialog, which allows you to specify the options for printing or copying graphs
- Copy Graph option is to print the graphic portion of the Power Spectral Display on the clipboard.
- Copy Page option is to print the Power Spectral Display window on the clipboard
- Save as Metafile option is to save the graph as a meta file
Example
Connect a loopback cable, transmit a tone of 1004 Hz into a timeslot on card 2, and observe the spectral display for the desired timeslot on card1. Adjust the sample size to increase or decrease the resolution of the spectrum of the sine wave. Experiment with options of the spectral display.
 Back to List of T1E1 Basic and Optional Applications Index Page
Back to List of T1E1 Basic and Optional Applications Index Page