GL Announces Simulation of Location Based Services in Mobile Networks (Part 1)
Welcome to another March 2017 issue of GL Communications' Newsletter providing information and insight into our Location Services (LCS) Test Suite to support simulation of location based services in GSM, UMTS, and LTE networks.
In this Part 1 of Location Services (LCS) Test Suite newsletter, we briefly discuss:
- the important elements, interfaces, and procedures in the location request and response in the GSM network
- how to test these using MAPS™ Lb and MAPS™ MAP IP (Lg and Lh) protocolsimulators

Location Services (LCS) Network Architecture
Overview
Location based services provide information about the geographic location of Mobile Equipment (ME) and is widely used in social networking, vehicle tracking, stolen assets tracking, emergency services, and many more. The information is expressed in latitude and longitude data that is represented in a well defined universal format.
Location service architecture specifies all the necessary network elements and entities, and their functionalities, interfaces, as well as communication messages, necessary to implement the positioning functionality in a cellular network.
The Location Services (LCS) architecture follows a client/server model with the Gateway Mobile Location Center (GMLC) acting as the server node providing information to external LCS Clients. All LCS clients communicate with this node to request positioning information. Additionally, the GSM network includes separate nodes, Service Mobile Location Center (SMLC) that resides within BSC and Location Measurements Units (LMU) that resides within BS, for calculating and updating the location measurements.
As depicted in the main diagram above, some of the important interfaces participating in the location request and response in the GSM network are:
- Lb interface - The BSC is accessible to the SMLC via the Lb interface
- Ls interface - The MSC/VLR is accessible to the SMLC via the Ls interface
- Lg interface - The MSC/VLR and SGSN is accessible to the GMLC via the Lg interface
- Lh interface - The HLR is accessible to the GMLC via the Lh interface
- Le interface - Interface between GMLC and LCS clients
Location estimation uses different positioning methodologies that are classified into network based and handset based methods. The main difference is that the network-based measurements do their calculations at the infrastructure, while the handset measurements do their calculations at the handset.
The standard positioning methods used in GSM network are:
- Cell Global Identification (CGI) (network based)
- Uplink Time Difference of Arrival (U-TDOA) (network based)
- A-GNSS (handset based)
- Enhanced Observed Time Difference (E-OTD) (handset based)
For further details on positioning methods, refer to LCS in GERAN 3GPP TS 43.059 v13.2.0 Rel13 document.
Simulation of LCS Procedures using MAPS™
GL’s MAPS™ LCS test suite comprises of multiple products working in tandem to support simulation of end-to-end location based services in GSM, UMTS, and LTE networks.
Specifically, to test location services in GSM network, GL’s MAPS™ MAP IP signaling emulator is enhanced to simulate LCS procedures over Lg and Lh interfaces using MAP signaling protocol. MS initiated Location Report Procedure is supported over Lg Interface between GMLC and MSC and network initiated Location Retrieval Procedure is supported over Lh Interface between GMLC and HLR.
Further, the MAPS™ Lb interface emulator supports Location Service Request procedure over Lb interface between BSC and SMLC using BSSMAP-LE signaling protocol. These are discussed briefly below.
GL's MAPS™ supports simulation of different Positioning methods and Position Estimation of a Mobile Stations (MS) in universal coordinates. The estimate is expressed in terms of the geographical shapes and is composed of the type of shape plus the encoding of the shape itself. The Location Estimate parameters such as Type of Shape and coordinates can be input through conventional user profiles or can be fetched from a CSV file every time it sends the location estimate to the client. This selection is to be made by the user.
If the selection is 'Profile' all the values present in the particular profile will be sent in the message response. If the selection is made as ‘CSV’, an entry from the csv file is loaded and all the values from the fetched record will be sent in the message response.
These coordinates indicate different position of MS at different intervals of time and report is sent either periodically at specified time duration or at once when requested.
Typical call flow simulation of location based services messages by MAPS™ is as shown below -
Complete Call Flow of LCS Procedures with MAPS™ Lb, and MAPS™ MAP IP (Lg, Lh) Emulators
Lg, Lh Interfaces
MAPS™ MAP IP supports both server and client simulation of Mobile Application Part (MAP) signaling protocol over Lg, Lh interfaces. It allows testing SGSN/MSC entities in UMTS/GSM network with GMLC and vice-versa.
Typical message exchanges over Lg and Lh interface is shown in the call flow below:
- MAP-Provide-Subscriber-Location - used by a GMLC to request the location and optionally, velocity, of a target UE
- MAP-Subscriber-Location-Report - used by a SGSN to provide the location of a target UE to a GMLC
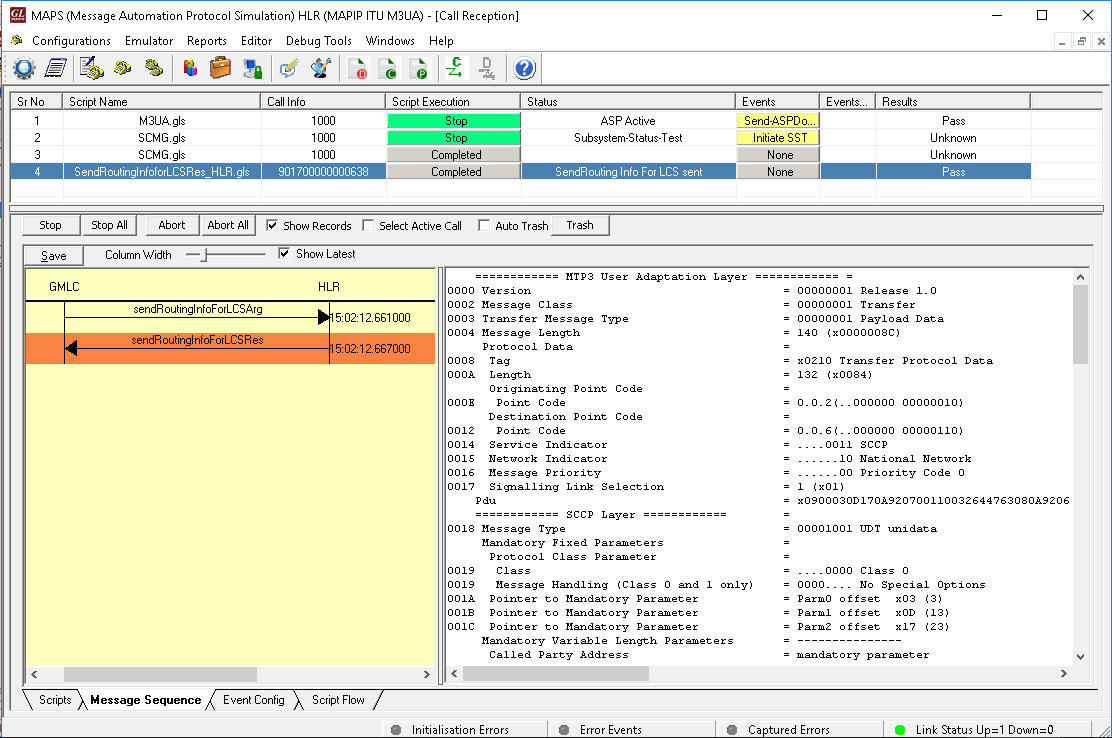
- MAP-Send-Routing-Info-for-LCS - used between the GMLC and the HLR to retrieve the routing information needed for routing LCS request to the servicing MSC/SGSN
The following screenshot depicts MAPS™ MAP IP configured as GMLC simulating LCS procedure over Lg interface.
Lb Interface
MAPS™ Lb interface emulator can simulate LCS network elements supporting positioning procedures over Lb interface between SMLC (Serving Mobile Location Center) and BSC (Base Station Center).
MAPS™ Lb supports Base Station System Management Application Part LCS Extension (BSSMAP-LE) message exchange between BSS and SMLC as per 3GPP TS 49.031 specification. The Lb interface, is transparent to all UE related and LMU (Location Measurement Utility) related positioning procedures. Typical Location Request procedure between BSS and SMLC is shown.
The following screenshot depicts MAPS™ Lb configured as SMLC simulating Lb interface BSSMAP-LE-Perform-Location-Request procedure.



 Back to Newsletter Index Page
Back to Newsletter Index Page