SGSN Pooling within GPRS Gb Interface Emulator
Welcome to another June 2017 issue of GL's Newsletter providing information and insight into our enhanced MAPS™ GPRS Gb Interface Emulator software that now supports the emulation of BSC and SGSN with SGSN Pooling feature where each BSC is connected to a SGSN pool.
Overview
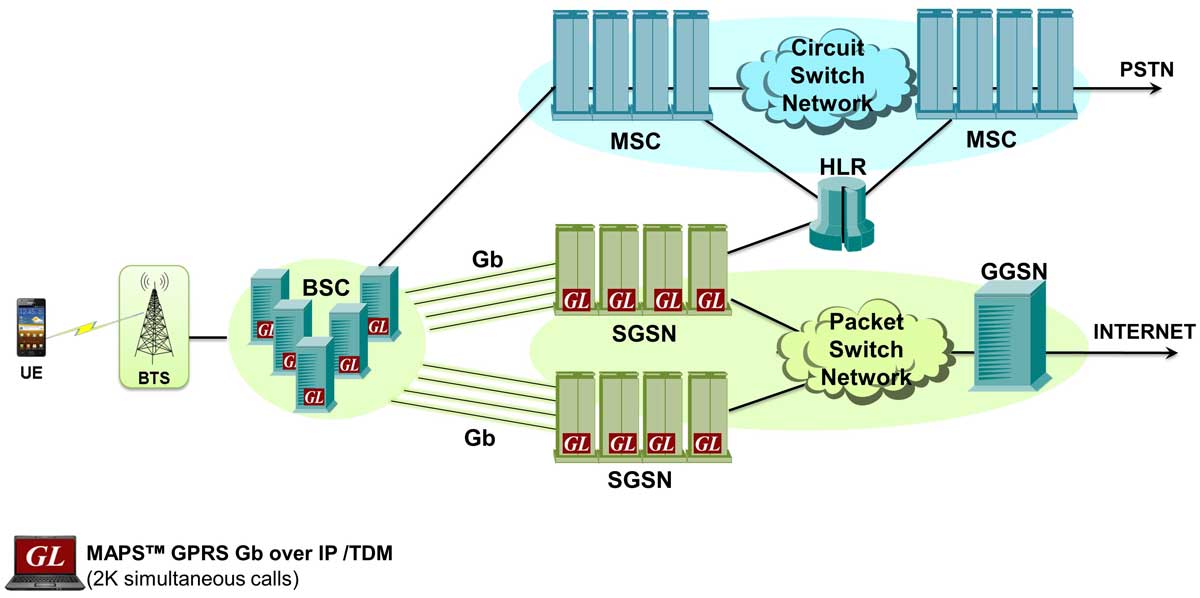
MAPS™ GPRS Gb supports Gb interface simulation between the Base Station Subsystem (BSS) and the Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) over IP transmission protocol. Emulation over Frame Relay transmission protocol will be supported in future.
With the latest release, MAPS™ GPRS Gb supports SGSN Pooling feature to permit customers emulate, test, and verify GPRS Gb functionality. Besides testing network elements (SGSN and BSS), the tester also involves error tracking, regression testing, and load testing/call generation. MAPS™ GPRS Gb interface Emulator supports various procedures including Network Service Control, Identity Check, Combined GPRS / IMSI Attach, and Routing Area Update. It can run pre-defined test scenarios against the interface test objects in a controlled & deterministic manner.
MAPS™ GPRS Gb Interface Emulator supports powerful utilities like Message Editor, Script Editor, and Profile Editor which allow new scenarios to be created or existing scenarios to be modified as per the protocol standards supported.
SGSN Pooling
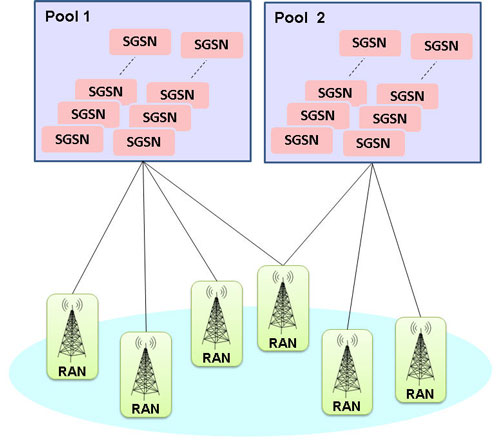
The SGSN in Pool solution overcomes the strict hierarchy which restricts the connection of a BSC node to just one SGSN. It introduces a new routing mechanism which allows a BSC belonging to an SGSN Pool connect to all SGSNs in that pool. This permits an MS roam freely without a need to change the serving SGSN.
An SGSN in the SGSN Pool serves all the routing areas (RAs) in the pool area and shares the traffic of this area between each other.
SGSN Pooling solution provides the following benefits:
- Increased Availability: With the introduction of Pool feature, Multiple SGSN nodes can be deployed in a network, and an instance of a single SGSN failure will not be an issue any more as another SGSN node within the Pool will serve the request from the BSCs.
- Increased Scalability: Easy to increase capacity by adding SGSN nodes to a Pool.
- Reduced Signaling and Increased Coverage Area: Coverage area served by the SGSN Pool would be large enough to decrease the Inter-SGSN routing area update procedures, handovers and relocations that help in reduced signaling.
SGSN Pooling
GL's MAPS™ GPRS Gb provides the following SGSN Pool features.
- User configurable number of SGSN Pool
- User configurable number of SGSN within a Pool
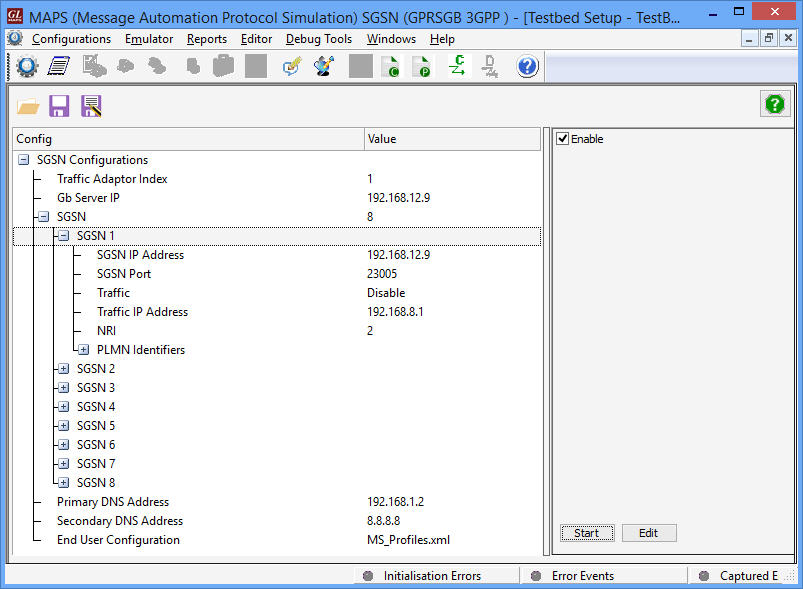
- SGSN Pool Identifier - Selection of SGSN Pool for each BSC
- NRI configuration at SGSN - The Network Resource Identifier (NRI) identifies uniquely an individual SGSN out of all SGSNs, which serve in parallel a pool-area.
- NAS Node Selection Function - Selects the specific SGSN to which initial session establishment request are routed.
- Load Balancing - selects appropriate SGSN and offloads the traffic available SGSNs in a pool, when the derived NRI does not map to indicated SGSN
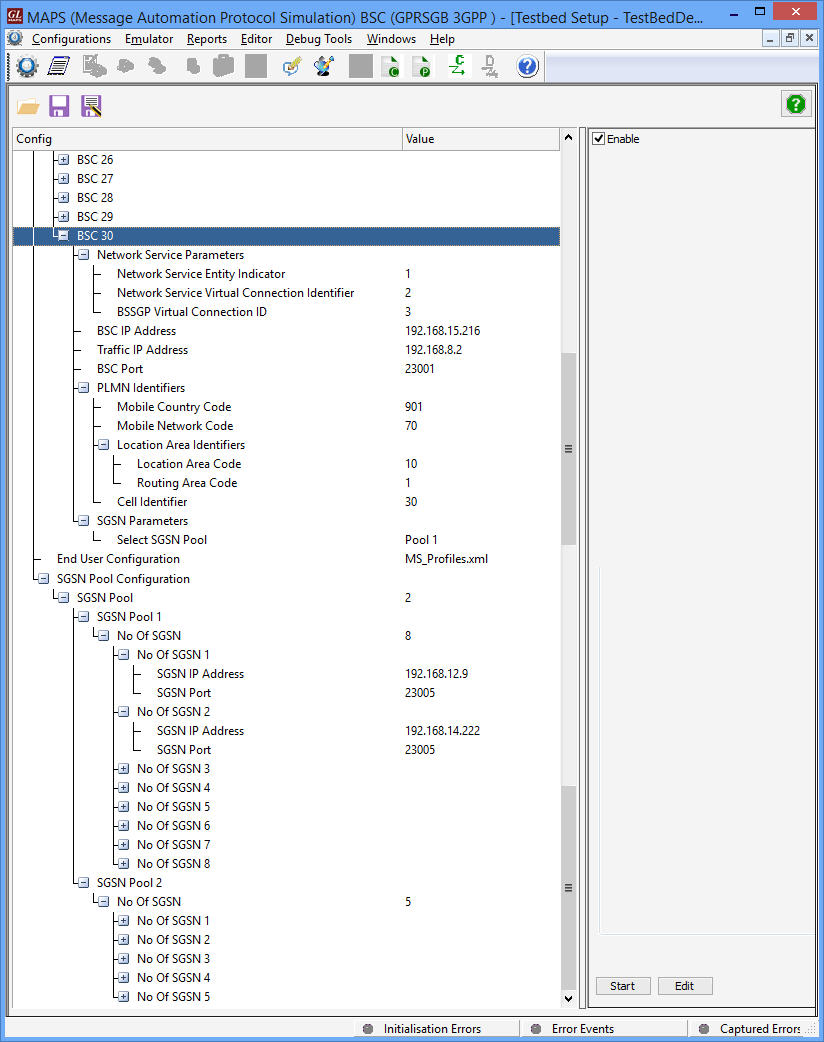
Test Configurations - BSCs and SGSNs
Supported Protocol Standards
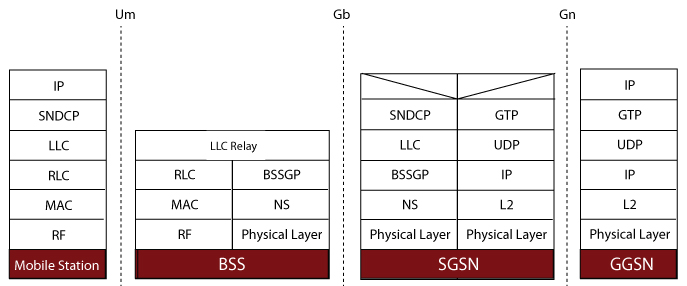
Gb Interface Protocol Standards
| Supported Protocols | Specification Used |
|---|---|
| BSSGP | 3GPP TS 08.18 V8.10.0 (2002-05) |
| LLC | 3GPP TS 04.64 V8.7.0 (2001-12) |
| NS (Network Service) | GSM 8.16 (ETSI TS 101 299 V8.0.0) |
| GMM | 3GPP 24.008 |
| SMG (GPRS Session Mgmt) | 3GPP TS 24.008 V5.16.0 (2006-06) (Release 5) |
| SNDCP | 3GPP TS 04.64 V8.7.0 (2001-12) |
Main Features
- Simulates Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) and Base Station Subsystem (BSS) elements in GPRS Gb interface over IP
- Simulates Control plane Gb mode
- Generates hundreds of Control Signaling (Load Testing)
- Generates and processes Network Service (NS), Base Station Subsystem GPRS Protocol (BSSGP), and various GPRS session procedure messages
- Supports Gb interface procedures including Network Service Control, Identity Check, Combined GPRS / IMSI Attach, and Routing Area Update
- Supports SGSN pooling to test and verify redundancy, load balancing, and scalability of network
- Insertion of impairments to create invalid messages
- Supports customization of call flows and message templates using Script and Message editors
- Supports scripted call generation and automated call reception
- Script based & protocol independent software architecture
- Provides Call Statistics and Events Status
Applications
- Complete analysis and simulation capability
- Provides fault insertion, and erroneous call flows testing capability
- Functional testing, Regression testing and Conformance testing of network elements
- Ready scripts make testing procedure simpler, less time consuming and hence time to market products
- QoS requests for greater or lesser bandwidth
Call Statistics
By default, all call handling scripts (irrespective of the type of the functions) are assessed by MAPS™ to provide statistical information about Total Calls, Active Calls, Completed Calls, Passed Calls, Failed Calls, and Calls/Sec. It is also possible to characterize the statistical information under different groups of call handling scripts under a unique heading. In addition, Call Generation and Call Reception windows provide useful call status & script execution results.
 Back to Newsletter Index Page
Back to Newsletter Index Page