GL Announces 911, E-911, & NG 911 Signaling Simulation & Monitoring
6th, Dec 2019
Welcome to another issue of GL Communications' Newsletter providing information and insight into our test, simulation, and monitoring systems for 911, E-911, and NG-911 networks, systems, and protocols. In this newsletter, we discuss protocol specifics of CAMA signaling in the 911 architecture and test solutions for the same.
Overview
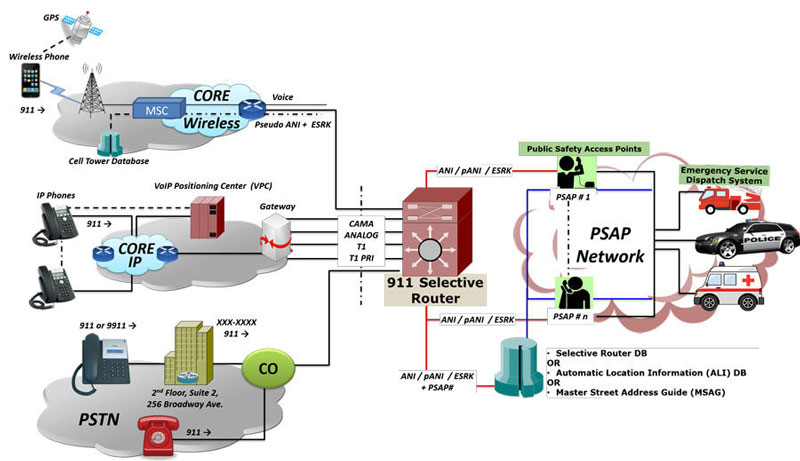
CAMA-Centralized Automatic Message Accounting is a special analog trunk originally developed for long-distance billing but is now mainly used for emergency call services: 911 and Enhanced 9-1-1 (E-911).
A CAMA trunk connects a carrier switch directly to a Selective Router (SR), a special 911 Switch that in turn connects to many Public Safety Access Points(PSAPs). PSAPs are call centers where agents answer emergency calls and dispatch police, firefighters, and ambulances. The Selective Router routes the call to the appropriate Public Safety Answering Point (PSAP) based on the calling party’s physical location which is obtained from the Automatic Number Identification (ANI) transmitted using MF tones, i.e. the calling number. For PSTN lines, a database lookup provides the physical location of callers against the ANI.
CAMA Trunks Connected to 911 Switch CAMA signaling is used for sending the calling party's Automatic Number Identification (ANI) to the 911 selective router. The ANI in the form of MF digits can be defined as: KP-I-NXX-XXXX-ST where,
|
 Signaling sequence for CAMA type trunks |
||
| CAMA Trunks Connected to the PSAP For an alternative configuration in Private Exchange Branches (PBX) where the CAMA trunks are connected directly to the PSAP, the ANI is defined as: KP-NPD-NXX-XXXX-ST where,
|
 Signaling Sequence for CAMA type trunks |
GL's Solution
CAMA Signaling Simulation and Monitoring is accomplished using MAPS™ CAS Emulator and MAPS™ FXO FXS Emulator hardware and software applications. All of these are strictly over a TDM or Analog network.
Both analog and digital (T1) CAMA simulations are supported. Analog simulation can be realized by using channel bank or using tProbe™ FXO FXS hardware, both specially configured for CAMA. Channel bank solution offers bulk calling up to 192 FXO/FXS ports. tProbe™ FXO FXS solution offers single port testing to test functionality of 911 selective router.
Analog CAMA Simulation via Channel Bank
For Analog simulation, MAPS™ CAS requires additional Channel Bank specially configured for CAMA. The tProbe™ T1 line is connected to Channel bank with FXO cards for interfacing to 2-wire equipment (911 selective router). Single FXO board within the channel bank can convert one digital T1 line into 8 Analog lines. MAPS™ CAS with Channel Bank can be used to simulate High density FXO supporting up to 96 Analog Channels.
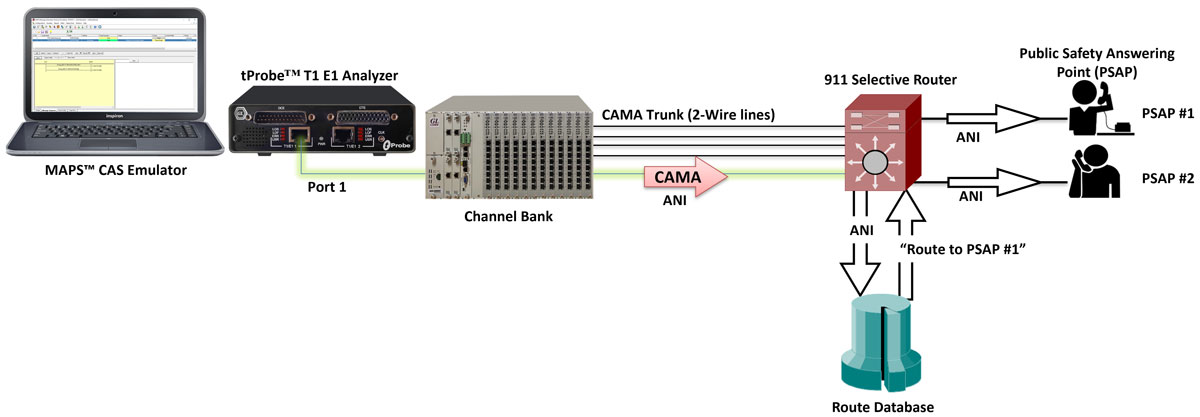
Analog CAMA Simulation
Analog CAMA Simulation via tProbe™ FXO and FXS
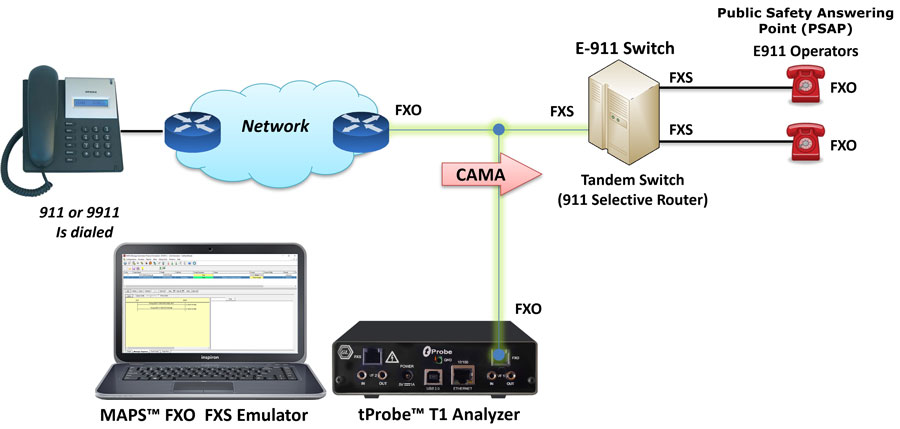
The tProbe™ FXO port can be directly connected to 911 selective router or PSAP on CAMA-type circuits for simulation of CAMA calls to the selective router or PSAP. The script will seize the line, wait for wink, dial ANI and wait for call connect.
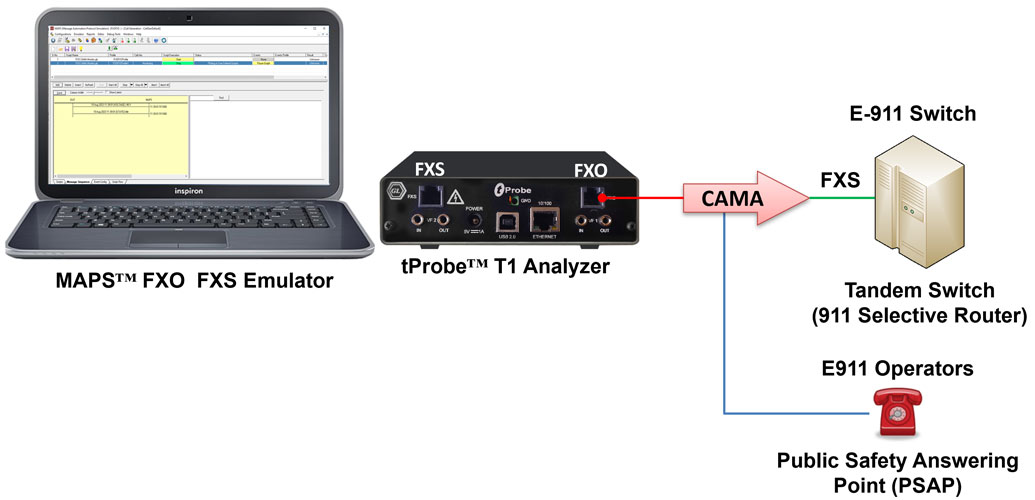
Originating CAMA Call Simulation (FXO ports)
The figure below shows tProbe™ FXS port connected to central office or selective router for terminating CAMA calls. The script will detect seizure from far side, provide wink, wait for ANI, and connect the call.
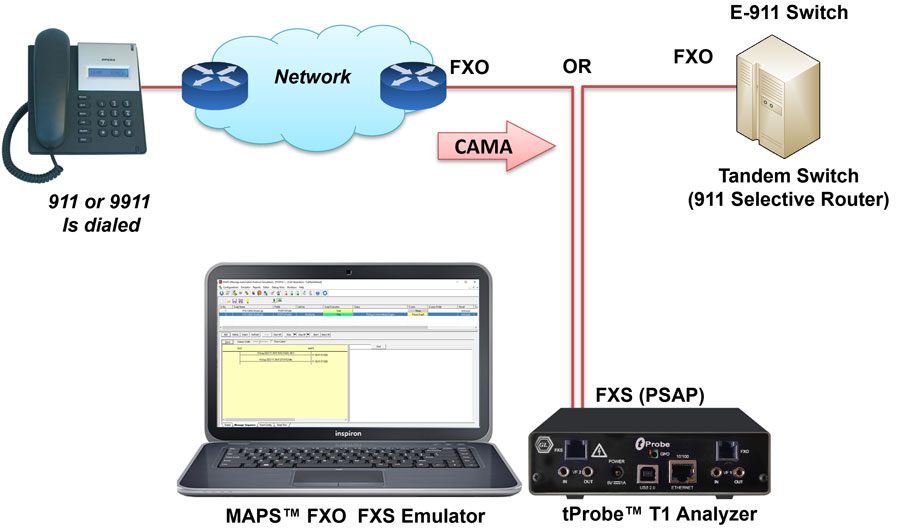
Terminating CAMA Call Simulation (FXS ports)
The MAPS™ FXO FXS Emulator application displays a real-time signaling sequence of the CAMA type trunk connected to the 911 Selective Route as shown below.
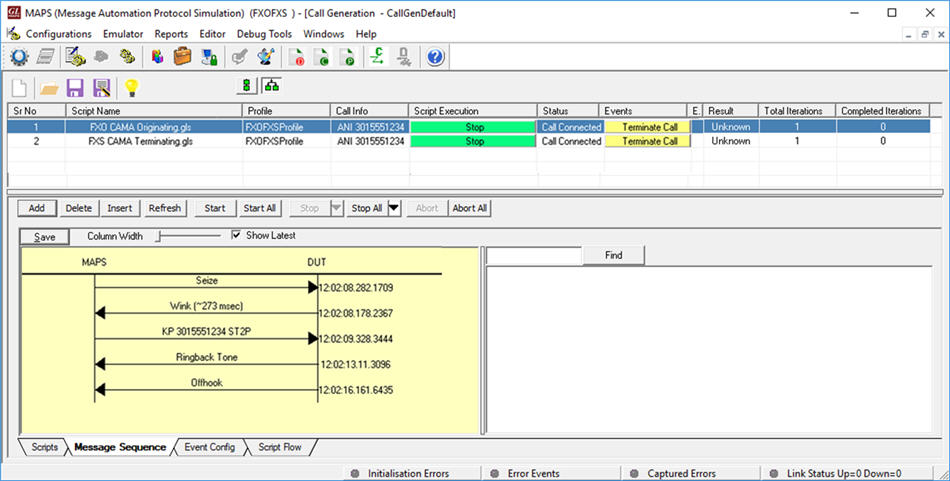
FXO CAMA Simulation Message Sequence
Digital CAMA Simulation

Digital CAMA Simulation
As shown in the above figure, MAPS™ CAS Emulator can be configured for CAMA signaling for emulation of 911 services on digital T1 trunks connected to the 911 Selective Router.
CAMA emulation capabilities include - seizure and wink start detection, onhook and offhook detection and MF digit (ANI) generation/detection.
The MAPS™ CAS Emulator application displays a real-time signaling sequence of the CAMA type trunk connected to the 911 Selective Router as shown below.

MAPS™ CAS Simulating CAMA Trunks Message Sequence
FXO Monitoring of CAMA Type Trunks for 911 Circuits
The tProbe™ FXO port can be tapped onto CAMA-type circuits for non-intrusive monitoring of 911 service. Monitoring capabilities include seizure and wink start detection, onhook and offhook detection and MF digit (calling party ANI) detection. A normal analog call is routed based on the destination (called party) phone number. However, 911 calls are routed based on the calling party number.
FXO Monitoring of CAMA type trunks using MAPS™ FXO FXS
MAPS™ FXO FXS Emulator displaying a real-time ladder diagram of the CAMA type trunk signaling sequence as captured by the FXO port. Typically, there are 5 CAMA signaling types based on the number of digits in ANI, these include, 7-digit transmission (kp-0-nxx-xxxx-st), 8-digit transmission (KP-npd-nxx-xxxx-st), 10-digit transmission (kp-0-npa-nxx-xxxx-st), 20-digit transmission (kp-0-npa-nxx-xxxx-st-kp-yyy-yyy-yyyy-st), and kp–2–st (indicates a failure to receive ANI).
The following call is monitoring a 10-digit ANI transmission.

Call monitoring process of a 10-digit ANI transmission
The monitoring script is used to monitor a CAMA line between the central office and selective router, or between the selective router and PSAP. This script continuously monitor line current and voltages of FXO and FXS ports. The script also monitors for seizure, wink, ANI, termination side offhook and plots the detected line voltage in User-Defined Graphs as shown below.

Line Voltage Graph
 Back to Newsletter Index Page
Back to Newsletter Index Page